
What's The Role Of OLT In GPON?
Do you ever wonder how the internet works? Well, one crucial component of fiber optic technology is the OLT in GPON. But what exactly is its role? Let's find out!
Imagine you're sending an important email or streaming your favorite show. Without the OLT, none of this would be possible.
So, let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of OLT and how it makes the magic happen!
The Role of OLT in GPON: Revolutionizing Fiber-Optic Broadband
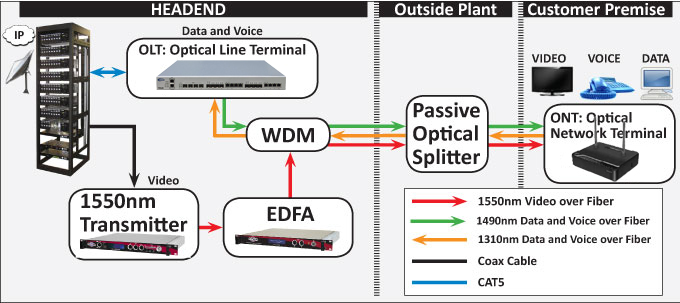
As the demand for high-speed internet continues to grow, so does the need for efficient and advanced broadband infrastructure. Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) technology has emerged as a game-changer, enabling the delivery of ultra-fast internet speeds over fiber-optic networks. At the heart of this transformative technology lies the Optical Line Terminal (OLT), a crucial component that plays a vital role in GPON networks. In this article, we will explore in-depth the role of OLT in GPON and its significance in revolutionizing fiber-optic broadband.
The Basics: What is GPON?
Before diving into the role of OLT in GPON, it's essential to understand the basics of GPON technology. GPON is a broadband access technology that utilizes fiber-optic cables to deliver high-speed internet, voice, and video services to end-users. GPON networks are capable of providing symmetrical speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps, making them ideal for both residential and business applications. The technology offers several advantages over traditional copper-based networks, such as higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances, and enhanced security.
1. What is an OLT?
The Optical Line Terminal (OLT) is a critical component in GPON networks, serving as the central hub that connects the service provider's network to the end-users. The role of OLT is to aggregate and manage the traffic coming from multiple Optical Network Units (ONUs), which are located at the customer's premises. The OLT acts as a mediator between the core network and the distribution network, ensuring smooth communication and efficient data transmission.
The OLT is responsible for several key functions in a GPON network:
- Authentication and authorization: The OLT verifies the identity of each ONU and grants access to the network based on authentication protocols.
- Bandwidth allocation: The OLT allocates dedicated bandwidth to each ONU, ensuring equal distribution and optimal performance.
- Traffic management: The OLT regulates and manages the flow of data between the core network and the ONUs, optimizing network efficiency.
The OLT also serves as the aggregation point for voice, video, and data services, enabling seamless delivery to end-users. Its high-performance processing capabilities and robust architecture make it the backbone of the GPON network, ensuring reliable and high-speed connectivity.
2. Key Components of an OLT
Understanding the key components of an OLT is crucial to comprehend its role in GPON networks. The main elements of an OLT include:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU handles all the processing tasks, including authentication, data routing, and traffic management.
- Optical Line Terminal Management and Control Card: This card oversees the overall management and control of the OLT, including software updates, performance monitoring, and network troubleshooting.
- Optical Line Terminal Line Card: The line card interfaces with the optical fiber network and converts the optical signals into electrical signals for transmission and vice versa.
- Power Supply Unit: The power supply unit ensures a stable and reliable power source for the OLT, minimizing downtime and maintaining uninterrupted services.
These components work together harmoniously to provide efficient and reliable connectivity to end-users in a GPON network.
3. Benefits of OLT in GPON
The role of OLT in GPON extends beyond its technical functions. It offers several benefits that contribute to the overall success and widespread adoption of GPON technology:
- Scalability: OLTs can be easily expanded to accommodate the growing number of subscribers, making it a cost-effective solution for service providers.
- Cost-efficiency: GPON networks, with OLT at their core, require less cabling and equipment compared to traditional copper-based networks, resulting in lower installation and maintenance costs.
- Enhanced user experience: OLTs ensure stable and high-speed internet connectivity, delivering unmatched user experiences for activities such as streaming, gaming, and cloud services.
- Future-proof technology: The flexibility and scalability of OLTs make them future-proof, able to adapt to emerging technologies and increasing bandwidth requirements.
The role of OLT in GPON networks is pivotal in transforming the broadband landscape, offering lightning-fast speeds and unprecedented reliability. As the demand for high-speed internet continues to soar, OLTs will continue to play a crucial role in meeting the ever-increasing bandwidth needs, shaping the future of connectivity throughout the world.
The Evolution of GPON and the Future of OLT
As technology advances and user demands evolve, GPON networks are continuously evolving to meet these changing requirements. The next generation of GPON, known as XGS-PON, offers even higher speeds and increased capacity, extending the capabilities of OLTs further. Here are three significant developments shaping the future of GPON and the role of OLT:
1. XGS-PON: Expanding OLT Capabilities
The deployment of XGS-PON, an enhanced version of GPON, enables service providers to deliver symmetrical speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This significant boost in performance is achieved by utilizing wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology, which allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple wavelengths over a single fiber-optic strand. OLTs in XGS-PON networks are equipped with enhanced processing power and sophisticated software, ensuring smooth handling of the increased bandwidth and advanced services.
2. OLT Virtualization: Driving Network Efficiency
OLT virtualization is another significant development that is revolutionizing GPON networks. With virtualization, the functions traditionally performed by physical OLTs are moved to a virtualized environment, enabling increased network agility and cost savings. Virtualized OLTs can be dynamically allocated and scaled based on demand, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware for every OLT. This approach enhances network efficiency, reduces operational costs, and provides greater flexibility to service providers.
3. Fiber Deep: Extending Reach and Capacity
Fiber Deep is an architectural approach that aims to bring fiber-optic connectivity closer to end-users. By deploying fiber deeper into the network, service providers can reduce the number of subscribers served by each OLT, thereby increasing overall capacity and improving performance. This strategy enables the delivery of higher speeds and enhanced quality of service, ensuring seamless connectivity for bandwidth-intensive applications. Fiber Deep, in combination with advanced OLT technologies, sets the stage for the future of GPON, catering to the exponential growth in data consumption and the emergence of new technologies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of OLT in GPON networks is fundamental to the delivery of high-speed internet, voice, and video services. OLTs act as the central hub, aggregating and managing the traffic from multiple ONUs, while also serving as the interface between the core network and the distribution network. With their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to provide enhanced user experiences, OLTs have revolutionized the broadband industry.
The evolution of GPON technology, along with advancements in OLT capabilities, promises a future of even faster and more efficient broadband networks. XGS-PON, OLT virtualization, and Fiber Deep are just a few examples of the developments that will shape the future of GPON and continue to push the boundaries of connectivity. Ultimately, the role of OLT in GPON will remain crucial, enabling the delivery of lightning-fast internet speeds and transforming the digital landscape for generations to come.
Key Takeaways: What's the role of OLT in GPON?
- An OLT (Optical Line Terminal) is a crucial device in GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network). It centrally controls and manages the distribution of data and voice signals.
- OLT serves as the interface between the Internet Service Provider (ISP) network and the customer's premises, converting optical signals into electrical signals that can be processed by various devices.
- OLT also performs key functions such as traffic management, authentication, and security to ensure a stable and secure connection for the users.
- With the help of OLT, multiple customers can be connected to a single fiber optic cable, optimizing resources and reducing costs for service providers.
- The OLT plays a vital role in enabling high-speed internet access, voice services, and video streaming in GPON networks, enhancing the overall communication experience for users.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about the role of OLT in GPON:
1. What is the purpose of the OLT in a GPON network?
The OLT (Optical Line Terminal) plays a crucial role in a GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) by acting as the main point of connection between the power, service, and distribution networks. It serves as the gateway for transferring data between the end-user devices and the service provider's network infrastructure.
The primary purpose of the OLT is to convert electrical signals from the service provider into optical signals for transmission over the fiber optic network. It also handles the optical signal modulation and demodulation, ensuring efficient data transmission and reception to and from the end-user devices connected to the GPON network.
2. How does the OLT manage multiple connections in a GPON network?
The OLT manages multiple connections in a GPON network through a process called time division multiplexing (TDM). It divides the available bandwidth into time slots and allocates them to the various connected end-user devices. Each device is assigned a specific time slot to transmit and receive data, ensuring that each connection has its dedicated resources.
Additionally, the OLT implements a technique called wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), which allows multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously over different wavelengths of light. This enables the OLT to handle a large number of connections without sacrificing speed or data throughput in the GPON network.
3. Can the OLT handle voice and video services in a GPON network?
Yes, the OLT is capable of handling voice and video services in a GPON network. It supports various protocols, such as VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) and IPTV (Internet Protocol Television), which allow for the transmission and delivery of voice and video data over the network.
By providing Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms, the OLT ensures that voice and video traffic receive priority treatment to minimize latency and ensure a smooth and uninterrupted user experience for these services in the GPON network.
4. What is the role of the OLT in network management and control in a GPON network?
The OLT plays a critical role in network management and control in a GPON network. It serves as the central point for monitoring and configuring the network. The OLT allows service providers to remotely manage and control various network elements, such as end-user devices, optical network units (ONUs), and optical splitters.
Through the OLT, service providers can perform tasks such as provisioning new services, monitoring network performance, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and implementing security measures to safeguard the network and its users in a GPON network.
5. How does the OLT ensure security in a GPON network?
The OLT ensures security in a GPON network through various mechanisms and protocols. It implements features such as encryption, authentication, and access control to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the data being transmitted over the network.
Additionally, the OLT provides security measures such as firewall protection, intrusion detection systems, and virtual LAN (VLAN) segregation to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate potential security threats in the GPON network. These security measures help create a safe and secure environment for the users and their data.
GPON Technology Fundamentals | Concepts of PON | GPON Architecture and Principles | GPON vs EPON.
Summary:
The OLT, or Optical Line Terminal, plays an important role in GPON technology. It acts as a central hub, connecting multiple homes or businesses to the internet through fiber optic cables. The OLT receives data from the connected devices and sends it across the network, allowing people to access the internet.
By using GPON technology, the OLT can support a large number of users and provide high-speed internet. It also helps to manage and control the network, ensuring that data is delivered efficiently and securely. So, next time you browse the internet, remember the vital role that the OLT plays in keeping you connected!
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote