
What's The Role Of An ONT In GPON?
Are you curious about the role of an ONT in GPON? Well, you've come to the right place! In this article, we'll explore what an ONT is and why it's an essential part of GPON technology.
So, what exactly is an ONT? It stands for Optical Network Terminal, and it's a device that connects your home or business to the fiber-optic network. Think of it as the bridge between your devices and the high-speed internet that flows through the fiber-optic cables.
But what makes the ONT so important in GPON? Well, with the ONT, you can enjoy lightning-fast internet speeds, crystal-clear voice calls, and high-definition video streaming. It's like having a superpower for your digital life!
Now that we've piqued your interest, let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of ONTs and explore their incredible role in GPON networks. So, buckle up and get ready for an exciting journey into the digital realm!
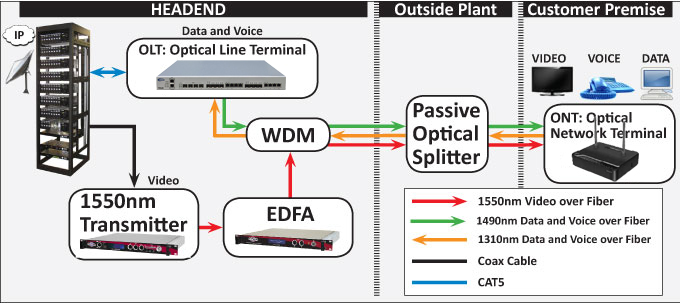
The Role of an ONT in GPON: Everything You Need to Know
Welcome to our in-depth guide on the role of an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) in Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON). In this article, we will explore the importance and functions of an ONT in delivering high-speed internet services to homes and businesses. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or someone seeking a better understanding of your internet connection, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the world of GPON and ONT technology.
What is an ONT?
An ONT, or Optical Network Terminal, is a crucial component in GPON networks. It serves as the interface between the fiber optic network and the customer's premises. Essentially, the ONT acts as a bridge that converts the optical signals transmitted through the fiber optic cables into electrical signals that can be used by the customer's devices, such as computers, smartphones, and smart TVs. The ONT is typically installed inside the customer's premises, often near the demarcation point where the fiber optic cable enters the building.
The ONT serves as the gateway for data, voice, and video services provided by the service provider. It enables high-speed internet connectivity, voice over IP (VoIP) telephony, and IPTV services. Additionally, the ONT may also include additional ports for Ethernet connections, allowing customers to connect wired devices directly to the network. Some advanced ONTs may even support Wi-Fi, providing wireless connectivity within the premises.
In summary, the ONT plays a vital role in connecting the customer's devices to the GPON network, enabling fast and reliable internet, voice, and video services.
How Does an ONT Work?
Now that we understand the basic function of an ONT let's dive deeper into how it works. When data is transmitted from the service provider's network, it is sent in the form of light pulses through the fiber optic cables. These light pulses are carried by the optical signal and are received by the ONT via the fiber optic port.
Once the optical signal reaches the ONT, it is converted into electrical signals that can be understood by the customer's devices. The ONT then distributes these electrical signals to the appropriate ports, which can be connected to computers, routers, telephones, or other devices.
For example, if a customer wants to access the internet, the ONT receives the data from the service provider's network, converts it into electrical signals, and forwards it to the customer's router. The router then further distributes the data to the connected devices, allowing them to access the internet.
Key Components of an ONT
While the specific features and capabilities of an ONT may vary depending on the service provider and the model, most ONTs consist of several key components:
- Optical Receiver: This component is responsible for receiving the optical signals transmitted through the fiber optic network.
- Media Converter: The media converter converts the optical signals into electrical signals that can be understood by the customer's devices.
- Power Supply: The power supply provides the necessary electrical power to the ONT.
- Ethernet Ports: These ports allow customers to connect wired devices directly to the network.
- Voice and Data Ports: These ports enable the connection of telephones and other devices for voice and data services.
- Wi-Fi Module (optional): Some ONTs include a built-in Wi-Fi module, allowing wireless connectivity within the premises.
Benefits of Using an ONT in GPON
The utilization of an ONT in GPON networks offers several benefits for both service providers and end-users:
- High-Speed Internet: ONTs enable the delivery of high-speed internet connections, providing faster download and upload speeds compared to traditional copper-based networks.
- Reliability: GPON networks using ONTs offer increased reliability since they are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation over long distances.
- Scalability: ONTs allow for easy scalability as they can be configured to support multiple services and can handle increased bandwidth demand as the network grows.
- Enhanced Service Offerings: With an ONT, service providers can offer a wide range of services, including voice over IP (VoIP) telephony and IPTV, enhancing the customer experience.
- Future-Proof Technology: GPON networks using ONTs provide a future-proof solution that can accommodate the increasing bandwidth requirements of emerging technologies.
ONT vs. Modem: What's the Difference?
It is important to note the difference between an ONT and a modem. While both devices serve as interfaces between the service provider's network and the customer's devices, they perform different functions.
A modem, short for modulator-demodulator, is responsible for converting the digital signals from the customer's devices into analog signals that can be transmitted over the service provider's network. On the other hand, an ONT converts the optical signals from the network into electrical signals that can be understood by the customer's devices.
In other words, a modem is used in traditional copper-based networks, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), while an ONT is used in modern fiber optic-based networks, such as GPON. While some ONTs may include modem functionality, they are not interchangeable devices.
Tips for Choosing an ONT
When selecting an ONT for your GPON network, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility: Ensure that the ONT is compatible with your service provider's network and supports the necessary services, such as data, voice, and video.
- Speed and Bandwidth: Look for an ONT that can support the desired internet speeds and handle the bandwidth requirements of your connected devices.
- Ports and Connectivity: Consider the number and type of ports required for your devices. If you have multiple wired devices, ensure that the ONT has enough Ethernet ports. If wireless connectivity is needed, opt for an ONT with a built-in Wi-Fi module.
- Reliability and Scalability: Choose an ONT from a reputable manufacturer that offers reliable performance and can handle future network expansion.
- Security Features: Look for an ONT that includes built-in security features, such as firewall protection and encryption, to ensure the safety of your network.
ONT Maintenance and Troubleshooting
The role of an ONT in GPON networks is crucial, and it is essential to perform regular maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure optimal performance. Here are some tips:
Perform Regular Software Updates
Keep your ONT's firmware up to date by regularly checking for software updates provided by the manufacturer or your service provider. Software updates often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements, ensuring a smooth and secure network experience.
Monitor Signal Strength and Quality
Keep an eye on the signal strength and quality of your ONT. Signal degradation can occur due to various factors, such as cable damage or environmental conditions. If you notice any inconsistencies or drops in signal quality, contact your service provider for assistance.
Troubleshoot Connection Issues
If you experience connection issues with your ONT, try the following troubleshooting steps:
- Restart the ONT: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve connection problems. Power off the ONT, wait for a few seconds, and then power it back on.
- Check Cabling: Ensure that all cables connecting your ONT and devices are securely plugged in and not damaged.
- Reset the ONT: If the issue persists, you may need to reset the ONT to its factory settings. Consult the user manual or contact your service provider for guidance on how to perform a reset.
- Contact Your Service Provider: If the above steps do not resolve the issue, reach out to your service provider's customer support for further assistance. They can help diagnose and resolve any network-related problems.
Enhance Your GPON Network with an ONT
With the growing demand for high-speed internet and advanced services, the role of an ONT in GPON networks becomes increasingly significant. Whether you're a service provider looking to deliver reliable connectivity to your customers or an end-user seeking a robust internet solution, understanding the functions and benefits of an ONT is essential. By choosing the right ONT and following maintenance best practices, you can ensure a seamless and enjoyable online experience.
Key Takeaways: What's the role of an ONT in GPON?
- An ONT, or Optical Network Terminal, is a device used in GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, to connect customer premises to the service provider's network.
- The primary role of an ONT is to convert the optical signal from the fiber optic network into electrical signals that can be used by customer devices.
- ONTs enable high-speed internet access, voice communication, video streaming, and other services for customers.
- ONTs typically have multiple ports to connect various devices, such as routers and telephones, to the GPON network.
- ONTs also provide important features like network management, security, and quality of service control to ensure smooth and reliable connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions section, where we'll answer common inquiries about the role of an ONT in GPON. Read on to discover more about this crucial component in a GPON network!
1. What is an ONT and what is its role in GPON?
An ONT, or Optical Network Terminal, is a device that connects to a fiber optic network and converts optical signals into electrical signals that can be used by end-user devices. In a GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network), the ONT serves as the customer's connection point to the network.
The ONT receives fiber optic signals from the OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and converts them into Ethernet or voice signals that can be used by devices such as computers, phones, or TVs. It essentially acts as the bridge between the fiber network and the customer's devices.
2. How is an ONT different from an OLT?
An ONT and an OLT (Optical Line Terminal) are two key components of GPON, but they have different roles. The OLT is responsible for aggregating and distributing data from multiple ONTs, while the ONT is the endpoint where the customer's devices connect to the network.
The OLT is typically located at the service provider's central office or data center, while the ONT is usually installed at the customer's premises. The OLT handles the transmission of data to and from the ONTs, while the ONT takes care of the conversion and distribution of signals within the customer's location.
3. Can an ONT support multiple services simultaneously?
Yes, an ONT is designed to support multiple services simultaneously. It can handle data, voice, and video services, allowing customers to access high-speed internet, make phone calls, and watch TV through a single ONT device.
The ONT is equipped with different ports to accommodate various types of connections, such as Ethernet ports for data, phone ports for voice, and coaxial or HDMI ports for video. This flexibility allows for the delivery of multiple services over a single fiber optic connection.
4. What are the key features of an ONT in a GPON network?
An ONT in a GPON network typically has several key features that make it an essential component:
- Fiber optic connectivity: It receives and transmits data over a fiber optic line, providing high-speed and reliable connections.
- Ethernet and voice support: It converts optical signals into Ethernet and voice signals, allowing for internet access and phone services.
- Multiple service ports: It offers various ports to connect different devices, including computers, phones, and TVs.
- Quality of Service (QoS) management: It prioritizes bandwidth allocation based on the type of service, ensuring consistent performance for different applications.
5. How is an ONT installed for a customer?
The installation process for an ONT varies depending on the service provider and the customer's location. In general, the ONT is mounted on a wall or placed on a flat surface near the customer's devices. It requires a power source, which can be connected to a standard electrical outlet.
Once the ONT is physically installed, the service provider technicians configure the device by connecting it to the fiber optic line and activating the necessary services. This typically involves setting up the appropriate connections and configuring any required settings, such as Wi-Fi network names and passwords. Once the ONT is properly installed and configured, the customer can start using the network services.
GPON Technology Fundamentals | Concepts of PON | GPON Architecture and Principles | GPON vs EPON.
Summary
So, what's the role of an ONT in GPON? Well, an ONT is like a translator between the fiber optic network and your home. It takes the optical signals from the network and converts them into electrical signals that your devices can understand. It also sends signals from your devices back to the network, allowing you to access the internet and make phone calls. In short, the ONT is an important piece of equipment that helps bring the power of fiber optic technology right to your doorstep.
But how does the ONT actually work? It's pretty simple, really. The ONT includes a modem that connects to the network and a router that distributes the internet connection throughout your home. It also has ports for you to plug in your devices, like computers or phones. So, when you're using the internet or making a call, it's thanks to the ONT that you're able to connect and communicate. So, now you know, the ONT plays a crucial role in making sure you can enjoy all the benefits of a high-speed fiber optic connection right in the comfort of your own home.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote