
What's The Lowdown On GPON Networks?
Are you curious about GPON networks and want to know what all the fuss is about? Well, you've come to the right place! In this article, I'll give you the lowdown on GPON networks in a way that's easy to understand.
So, what's the deal with GPON networks? GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is a type of fiber-optic network that revolutionizes the way we connect to the internet. It's like upgrading from a bicycle to a supersonic jet!
With GPON, data is transmitted using light signals through ultra-thin strands of glass, allowing for super-fast internet speeds and greater bandwidth. It's like having a highway dedicated solely to your internet traffic, ensuring a smooth and speedy online experience.
If you're ready to dive deeper into the world of GPON networks, buckle up and get ready for an informative and exciting journey. Let's unravel the mysteries behind this innovative technology and discover how it's transforming the way we stay connected.
The Lowdown on GPON Networks
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on GPON networks. In today's digital age, high-speed internet connectivity is a necessity, and Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) technology is revolutionizing the way we access the internet. In this article, we will dive into the world of GPON networks, exploring what they are, how they work, and the benefits they offer. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or simply curious about the technology behind your internet connection, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to understand GPON networks.
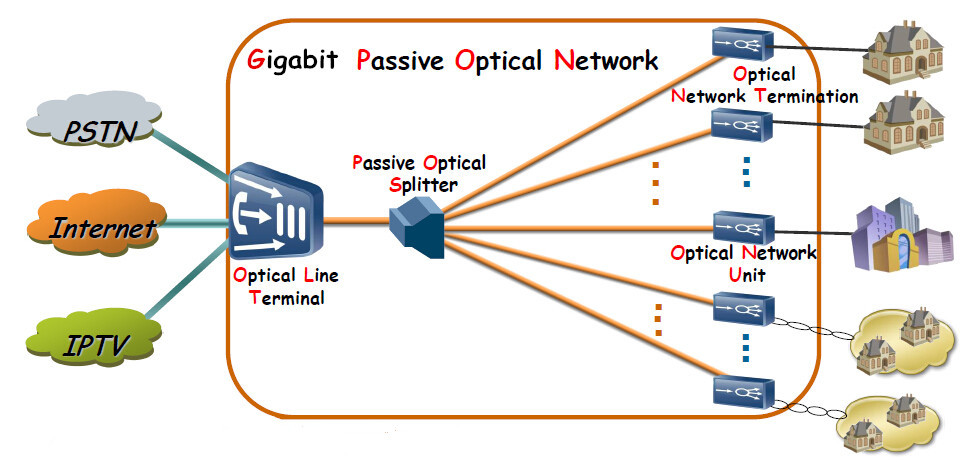
How do GPON Networks Work?
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is a fiber-optic communication technology that uses a single strand of fiber to deliver high-speed internet, voice, and video services to end-users. The network architecture consists of an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) located at the service provider's central office and an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) installed at the customer's premises.
The OLT acts as the central hub of the GPON network. It receives the data from the service provider's network and converts it into an optical signal that is sent over the fiber-optic cable to the ONT. The ONT then converts the optical signal back into electrical signals that can be used by the customer's devices, such as computers, phones, and televisions.
GPON networks use a technology called wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) to enable multiple users to share a single fiber-optic cable. WDM allows different wavelengths of light to be transmitted concurrently on the fiber, enabling high-speed downstream and upstream communication. This ensures fast and reliable internet access for multiple users simultaneously.
The Benefits of GPON Networks
GPON networks offer numerous benefits over traditional copper-based networks. Here are some of the key advantages:
- High-speed internet: With symmetrical upstream and downstream data rates of up to 2.488 Gbps, GPON networks provide incredibly fast internet speeds, allowing for seamless streaming, gaming, and other bandwidth-intensive activities.
- Increased bandwidth: GPON networks have a higher capacity for data transmission compared to copper-based networks. This enables service providers to offer a wider range of services, including high-definition television, video-on-demand, and cloud-based applications.
- Cost-effective: GPON networks offer cost savings for service providers due to the use of fiber-optic infrastructure. Fiber-optic cables have a longer lifespan, are less susceptible to interference, and require less maintenance compared to traditional copper infrastructure.
- Scalability: GPON networks are highly scalable, allowing service providers to easily add new users and expand their network coverage without significant investment in additional infrastructure.
- Reliability and resilience: Fiber-optic cables used in GPON networks are more resistant to environmental factors such as electromagnetic interference, lightning, and power surges, resulting in a more reliable and resilient network connection.
GPON Networks vs. Traditional Copper-based Networks
GPON networks and traditional copper-based networks have fundamental differences in terms of technology and performance. Here's a comparison:
| GPON Networks | Traditional Copper-based Networks | |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 2.488 Gbps | Up to 100 Mbps |
| Bandwidth | High capacity for data transmission | Limited bandwidth |
| Distance | Up to 20 kilometers | Up to a few hundred meters |
| Reliability | Less susceptible to interference | More susceptible to interference |
| Maintenance | Requires less maintenance | Requires regular maintenance |
From the comparison, it is clear that GPON networks offer significantly higher speeds, greater bandwidth, longer distance coverage, and greater reliability compared to traditional copper-based networks. These advantages make GPON networks the preferred choice for high-speed internet connectivity.
Factors to Consider When Implementing a GPON Network
When considering the implementation of a GPON network, there are several factors to take into account:
1. Coverage area: Determine the extent of the network coverage required, taking into consideration the number of potential users and their geographical distribution.
2. Equipment selection: Choose reliable and compatible OLT and ONT equipment from reputable vendors to ensure seamless integration and future scalability.
3. Bandwidth allocation: Plan the allocation of available bandwidth to meet the demands of users, considering factors such as peak usage hours and the type of services offered.
4. Network redundancy: Implement redundancy measures to ensure network reliability, such as redundant power supplies and backup connections to avoid single points of failure.
5. Security: Implement robust security measures to protect the network from unauthorized access and potential threats, such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPON networks have revolutionized the way we access high-speed internet. With their incredible speeds, increased bandwidth, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and reliability, GPON networks offer a wide range of benefits over traditional copper-based networks. When considering the implementation of a GPON network, it is important to consider factors such as coverage area, equipment selection, bandwidth allocation, network redundancy, and security to ensure a successful and efficient deployment. With GPON networks, users can enjoy fast and reliable internet connectivity, enabling seamless access to digital services and applications.
Key Takeaways: What's the lowdown on GPON networks?
- GPON networks, or Gigabit Passive Optical Networks, are a type of fiber-optic telecommunications technology.
- They use passive optical splitters to distribute internet signals to multiple users.
- GPON networks offer high-speed internet connections, with symmetrical upload and download speeds.
- They are commonly used in residential and business settings for internet access and other services.
- GPON networks provide reliable and efficient communication, supporting various applications like video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about GPON networks along with their answers:
1. How does a GPON network work?
A GPON network, which stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, uses fiber optic cables to deliver high-speed internet, TV, and telephone services to subscribers. It works by dividing the fiber optic cables into multiple splits, allowing each split to serve multiple subscribers. The network uses passive splitters to distribute data signals from the central office to the subscribers' premises.
At the central office, an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) converts electrical signals into optical signals, which are then transmitted through the fiber optic cables. At the subscribers' premises, an Optical Network Unit (ONU) receives the optical signals and converts them back into electrical signals, providing internet access and other services to the subscribers.
2. What are the benefits of GPON networks?
GPON networks offer several benefits over traditional networks:
Firstly, they provide much higher bandwidth, allowing for faster internet speeds and improved performance. This is especially beneficial for bandwidth-intensive activities such as streaming high-definition videos or online gaming.
Secondly, GPON networks can support a large number of subscribers on a single fiber optic cable, reducing the need for costly infrastructure upgrades. This makes it a cost-effective solution for service providers.
Lastly, GPON networks are highly reliable and offer symmetrical upload and download speeds, ensuring a consistent user experience. They also have the flexibility to support various services, such as voice, data, and video, all on a single network.
3. Is a GPON network different from a traditional Ethernet network?
Yes, GPON networks are different from traditional Ethernet networks in several ways. While Ethernet networks use copper-based cables to transmit signals, GPON networks use fiber optic cables, which can transmit data over longer distances without loss of signal quality. This makes GPON networks ideal for serving geographically dispersed areas.
In terms of bandwidth, GPON networks offer much higher speeds compared to traditional Ethernet networks. They can deliver gigabit speeds to individual subscribers, while Ethernet networks typically offer lower speeds.
Furthermore, GPON networks use a passive optical architecture, meaning they require less active equipment in the network, reducing power consumption and maintenance costs.
4. Can I use my current modem/router with a GPON network?
No, you cannot use your current modem/router with a GPON network. GPON networks require specific equipment called an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) or an Optical Network Unit (ONU) to connect to the fiber optic cable and convert the optical signals into electrical signals that your devices can use.
You will need to contact your service provider to obtain the necessary ONT or ONU device, which they will install at your premises. This new equipment will replace your current modem/router and enable you to connect to the GPON network.
5. Is a GPON network available everywhere?
GPON networks are not available everywhere at the moment. Their deployment depends on the infrastructure investments made by service providers in each specific area. GPON networks are more commonly found in urban and suburban areas where there is a higher density of potential subscribers.
However, the availability of GPON networks is gradually increasing as service providers expand their coverage. It's best to check with your local service providers or internet service providers to determine if GPON networks are available in your area.
What is PON - ( Passive Optical Networks Explained )
Summary
So, to sum it up, GPON networks are a type of high-speed internet connection that use fiber optics. They offer super fast download and upload speeds, allowing you to stream videos, play games, and browse the web without any lag. GPON networks are more reliable than traditional broadband connections and can support multiple devices at once. They are becoming increasingly popular and are likely to be the future of internet connectivity. So, if you're looking for a fast and reliable internet connection, GPON networks are definitely worth considering.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote