
What's The Difference Between GPON And EPON?
What's the difference between GPON and EPON? Let's dive into the world of internet connections and discover the contrasting features of these two technologies. If you've ever wondered how data travels from point A to point B, you've come to the right place. Get ready to explore the intriguing disparities between GPON and EPON!
In a world where internet connections are vital, GPON and EPON play essential roles. GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, and EPON, or Ethernet Passive Optical Network, are both systems that deliver high-speed internet access to homes and businesses. But what sets them apart? Join us on a journey of discovery as we unravel the distinctions between these two remarkable technologies!
From data transmission methods to network architecture, GPON and EPON offer distinct approaches to delivering internet services. Whether you're a tech-savvy individual or simply curious about the inner workings of the World Wide Web, understanding the differences between GPON and EPON will satisfy your thirst for knowledge. So fasten your seatbelt and get ready for a thrilling exploration into the world of internet connectivity!
When it comes to broadband communication technologies, GPON and EPON are often compared. GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, and EPON, or Ethernet Passive Optical Network, differ in their architecture and technical specifications. GPON offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances, making it suitable for larger networks. On the other hand, EPON provides lower latency and lower deployment costs, making it more cost-effective for smaller networks. Both technologies have their advantages and suit different network requirements.
Understanding the Difference Between GPON and EPON: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's digital age, high-speed internet connectivity is a necessity for households and businesses alike. Two popular technologies that provide this connectivity are GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) and EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network). Although they serve the same purpose, there are some key differences between the two. In this article, we will delve into the details of GPON and EPON, comparing their features, advantages, and use cases. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of which technology suits your needs best.
1. Introduction to GPON
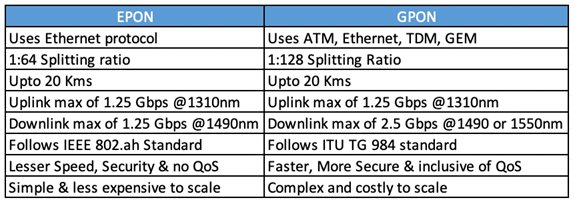
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is an optical distribution network technology that uses fiber optic cables to transmit data signals. It employs a point-to-multipoint architecture, allowing multiple users to share the same fiber optic line. GPON operates using Optical Line Terminals (OLTs) and Optical Network Units (ONUs) to facilitate communication between the service provider and the end-user. One of the key advantages of GPON is its ability to provide high bandwidth capacity, making it ideal for applications that require large data transfers, such as video streaming and online gaming.
GPON uses a time division multiplexing (TDM) technique, where data is divided into time slots, allowing for efficient transmission over the fiber optic line. This technology offers symmetrical speeds, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same. Moreover, GPON supports long distances without significant loss in signal quality. These characteristics make GPON a preferred choice for organizations and enterprises that demand reliable and high-performance internet connectivity.
2. Advantages of GPON
There are several advantages to using GPON technology:
1. High Bandwidth Capacity: GPON provides gigabit-level speeds, making it suitable for bandwidth-intensive activities such as video streaming, cloud applications, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
2. Cost-effective: Due to the shared infrastructure, GPON allows service providers to deliver high-speed internet at a lower cost per subscriber, making it an economical choice for both providers and users.
3. Reliability: GPON uses fiber optic cables, which are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference, ensuring a stable and reliable connection.
4. Scalability: GPON has a high scalability potential, allowing service providers to expand their network easily to accommodate more subscribers and future growth.
5. Security: Fiber optic cables used in GPON are more secure compared to traditional copper-based connections, as they are difficult to tap or intercept.
6. Energy Efficiency: GPON requires less power consumption compared to other broadband technologies, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced carbon footprint.
3. Introduction to EPON
EPON, or Ethernet Passive Optical Network, is another optical distribution network technology that uses fiber optic cables for data transmission. Unlike GPON, EPON follows an Ethernet-based architecture, using Ethernet frames for communication between the service provider and the end-user. EPON utilizes an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and Optical Network Units (ONUs), similar to GPON, to establish connectivity. EPON is commonly used in residential and small to medium-sized business environments.
One significant advantage of EPON is its compatibility with existing Ethernet networks. This allows for seamless integration with Ethernet-based devices and systems. Additionally, EPON supports both symmetric and asymmetric data transmission, offering the flexibility to allocate different bandwidths for upload and download activities. With its simplicity, affordability, and familiar Ethernet-based infrastructure, EPON is a popular choice for residential and small business users looking for high-speed internet connectivity.
4. Advantages of EPON
EPON offers several advantages for users and service providers:
1. Cost-effectiveness: EPON utilizes Ethernet components, which are widely available and relatively inexpensive. This makes EPON an affordable option for residential and small business users.
2. Compatibility: EPON seamlessly integrates with existing Ethernet networks and devices, avoiding the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades.
3. Flexible Bandwidth Allocation: EPON allows for customizable asymmetric bandwidth allocation, enabling users to optimize their internet connection based on their specific needs.
4. Wide Range of Applications: EPON supports various services, including voice-over-IP (VoIP), video conferencing, and cloud-based applications. This versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of residential and business applications.
5. Ease of Installation: EPON is relatively easy to install and configure, requiring minimal technical expertise. This simplifies the deployment process for service providers.
GPON vs. EPON: A Detailed Comparison
Now that we have explored the basics of GPON and EPON, let's dive into a detailed comparison of the two technologies.
1. Speed and Bandwidth
Both GPON and EPON offer high-speed internet connectivity, but there are some differences in terms of speed and bandwidth allocation. GPON provides symmetrical speeds, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same, typically ranging from 622 Mbps to 2.488 Gbps. EPON, on the other hand, supports both symmetrical and asymmetrical bandwidth allocation, allowing for different upload and download speeds. EPON typically offers speeds ranging from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps.
GPON
GPON offers symmetrical speeds ranging from 622 Mbps to 2.488 Gbps, making it ideal for applications that require symmetrical bandwidth, such as video conferencing and cloud-based services.
EPON
EPON supports both symmetrical and asymmetrical bandwidth allocation, providing flexibility in assigning different speeds for upload and download activities. This makes EPON suitable for applications where the upload speed is not as critical, such as residential internet usage.
In terms of raw speed, EPON has a higher maximum speed ceiling, reaching up to 10 Gbps, whereas GPON typically caps at 2.488 Gbps. However, it is important to note that these maximum speeds are theoretical and may not be achievable in real-world scenarios due to various factors such as network congestion and hardware limitations.
2. Reach and Coverage
The reach and coverage of GPON and EPON networks depend on several factors, including the quality of the fiber optic cables and the number of optical splitters used in the network infrastructure. In general, both GPON and EPON can cover extended distances without significant signal degradation. However, there are differences in terms of reach and coverage capabilities.
GPON
GPON technology allows for longer distances between the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and Optical Network Units (ONUs) without significant loss in signal quality. Typically, GPON can cover distances up to 20 kilometers (12.4 miles), making it suitable for larger deployments and network expansions.
EPON
EPON, on the other hand, has a shorter reach compared to GPON. It can cover distances up to 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) without requiring signal amplification. Although this is shorter than GPON, EPON is often used in smaller network environments, such as residential areas and small to medium-sized businesses, where the coverage requirements are not as extensive.
3. Scalability
Scalability is an essential consideration when choosing a fiber optic network technology. Both GPON and EPON provide scalability options, but there are differences in their expansion capabilities.
GPON
GPON has excellent scalability potential, allowing service providers to expand their networks easily. The architecture of GPON supports a maximum of 128 ONUs connected to a single OLT. This scalability is beneficial in scenarios where future growth and increased subscriber capacity are anticipated.
EPON
EPON also offers considerable scalability options. An EPON network supports up to 1024 ONUs connected to a single OLT, providing significant expansion capabilities. This makes EPON suitable for applications where a large number of users need to be accommodated, such as densely populated residential areas.
Overall, both GPON and EPON provide scalability options to meet the demands of growing networks. The choice between the two technologies depends on the specific requirements of the deployment, such as the expected number of users and network reach.
4. Compatibility and Interoperability
The compatibility and interoperability of GPON and EPON systems with existing network infrastructures and devices are crucial factors to consider.
GPON
GPON technology is not backward compatible with Ethernet-based networks. Therefore, deploying GPON may require additional investment in infrastructure upgrades to support its connectivity requirements. GPON uses a proprietary encapsulation method, making it incompatible with standard Ethernet frames.
EPON
EPON, on the other hand, is inherently compatible with Ethernet-based networks. It uses standard Ethernet frames for communication, making it easy to integrate with existing Ethernet networks and devices. This compatibility translates into reduced costs and simplified deployment processes.
In terms of interoperability, both GPON and EPON comply with international standards, ensuring that certified equipment from different manufacturers can seamlessly operate together. This interoperability allows for vendor independence and flexibility in selecting equipment and components.
The right choice for you
Now that we have explored the differences between GPON and EPON, it is essential to consider your specific requirements to determine which technology is the right choice for you. Here are some key points to consider:
1. If you require symmetrical bandwidth, high scalability, and the ability to cover long distances, GPON may be the ideal choice for you. GPON is suitable for large-scale deployments, enterprises, and organizations that demand high-performance and reliable connectivity.
2. If you value compatibility with existing Ethernet networks, affordability, and flexibility in bandwidth allocation, EPON may be the best option for you. EPON is suitable for residential areas, small to medium-sized businesses, and applications where a cost-effective solution is required.
To make an informed decision, we recommend consulting with a network provider or a professional in the field who can assess your specific requirements and offer expert advice tailored to your needs.
In conclusion, both GPON and EPON technologies provide high-speed internet connectivity using fiber optic cables. While GPON focuses on symmetrical speeds, scalability, and long-distance coverage, EPON prioritizes compatibility with Ethernet networks, cost-effectiveness, and flexible bandwidth allocation. By understanding the strengths and differences of both technologies, you can choose the right option to meet your internet connectivity needs.
Key Takeaways: What's the difference between GPON and EPON?
- GPON and EPON are two different types of fiber-optic network architectures.
- GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, while EPON stands for Ethernet Passive Optical Network.
- GPON uses a point-to-multipoint architecture, meaning one optical line terminal (OLT) serves multiple optical network units (ONUs).
- EPON, on the other hand, uses a point-to-point architecture, with each ONU having a dedicated connection to the OLT.
- GPON offers higher bandwidth and supports longer distances compared to EPON.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our Frequently Asked Questions page, where we'll help you understand the difference between GPON and EPON technologies. Below, we have provided answers to some common queries to shed light on this topic.
1. How do GPON and EPON differ in terms of technology?
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, and EPON, or Ethernet Passive Optical Network, are both fiber-optic network technologies. The main difference lies in the protocols they use. GPON utilizes Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) for communication, while EPON uses Ethernet Protocol. This distinction affects the way data is packaged and transmitted between the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and the Optical Network Unit (ONU).
In a nutshell, GPON is an older technology with a well-established standard, while EPON is a newer and more flexible alternative with a simpler architecture. GPON uses a Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)-based approach, resulting in a fixed bandwidth allocation scheme. On the other hand, EPON employs a Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP) architecture, allowing for dynamic bandwidth allocation to different users.
2. Which one is faster, GPON or EPON?
In terms of raw speed, both GPON and EPON offer comparable bandwidth capacities. They can provide gigabit speeds, allowing for efficient data transmission. However, GPON and EPON differ in terms of downstream and upstream speeds. GPON typically provides asymmetric speeds, meaning the downloading speed is faster than the uploading speed. EPON, on the other hand, offers symmetric speeds, providing the same throughput for both downloading and uploading.
It's important to note that the actual speed you experience will depend on various factors, including the network infrastructure, equipment, and service provider. Both GPON and EPON can deliver high-speed internet, but other factors may influence the overall performance.
3. Are GPON and EPON interoperable?
While GPON and EPON are not directly compatible with each other, it is possible to achieve interoperability through the use of certain gateway devices or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs). These devices act as mediators, allowing GPON and EPON networks to communicate with each other.
Interoperability is particularly important for service providers that want to transition from GPON to EPON or vice versa, without having to replace all their network infrastructure. By leveraging interoperability solutions, service providers can gradually migrate their networks while ensuring continuity of service for their customers.
4. Which technology is more widely adopted, GPON or EPON?
GPON has been in use for a longer period of time and has achieved wider adoption globally compared to EPON. Many service providers, especially in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, have deployed GPON networks extensively. The technology has proven to be reliable and offers decent performance for residential and business purposes.
However, EPON has gained significant traction in certain regions, particularly in Japan, China, and South Korea. EPON's simpler architecture and support for Ethernet have made it popular in these markets, especially for enterprise and business applications. As the demand for fiber-optic networks grows globally, the adoption of both GPON and EPON continues to increase.
5. Which technology is better for residential use, GPON or EPON?
Both GPON and EPON technologies are well-suited for residential use, depending on the specific requirements and infrastructure. GPON's mature standard and widespread adoption make it a reliable choice for delivering high-speed internet to homes. Its asymmetric speed profile, with faster download speeds, is generally sufficient for typical residential usage patterns.
On the other hand, EPON's symmetric speed profile and simpler architecture can offer advantages in residential settings where upload speeds are more important, such as for video conferencing or cloud backups. Additionally, EPON's flexibility and potential for cost-effectiveness make it an appealing option for smaller-scale deployments like residential areas or apartment complexes.
EPON vs. GPON Which One Is Better?Difference Between EPON and GPON
Summary
So, to sum it up, GPON and EPON are two different types of optical network technologies.
GPON uses a time division multiplexing (TDM) method, while EPON uses an Ethernet protocol.
They have different speed capabilities, with GPON offering higher speeds.
GPON is more commonly used for residential and small business connections, while EPON is popular in larger enterprise networks.
Ultimately, both GPON and EPON have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them depends on specific network requirements.
But now you know that they exist and what sets them apart!
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote