
What Does GPON Stand For?
GPON, have you ever heard of it? Wondering what those four letters stand for? Well, let's unveil the mystery together! GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. Cool, right? But what does that actually mean? Allow me to break it down for you.
Imagine a super-fast internet connection that can reach incredible speeds. That's what GPON is all about. It's a technology that uses optical fibers to transmit data at lightning-fast speeds, making your internet experience smoother than ever before. With GPON, you can say goodbye to those annoying buffering moments and hello to seamless streaming and gaming.
Now that you know what GPON stands for, you're probably wondering how it works. Don't worry, I've got you covered. In a nutshell, GPON works by sending data through a network of optical fibers using light, rather than traditional copper wiring. It's like a superhighway for your internet connection! And the best part? GPON can handle large amounts of data over long distances, providing fast and reliable internet access to homes and businesses alike.
So, whether you're a tech enthusiast or simply curious about the latest internet innovations, understanding what GPON stands for is a great starting point. Get ready to dive into the world of fast and reliable internet connections as we explore the wonders of GPON together! Let's get started, shall we?
What does GPON stand for?
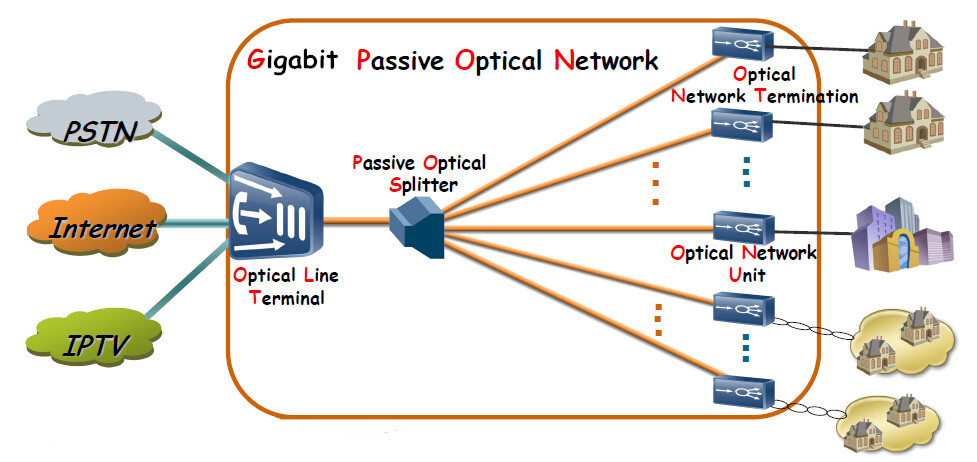
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It is a telecommunications network that uses fiber optic cables to transmit data at high speeds. GPON technology is widely used for delivering internet and other communication services to homes, businesses, and institutions. Unlike traditional copper-based networks, GPON offers faster and more reliable connectivity, making it an essential part of modern telecommunications infrastructure.
How does GPON work?
GPON operates by using a single strand of fiber optic cable to transmit data in both directions. This is achieved through a process called wavelength division multiplexing, which allows multiple signals of different wavelengths to travel along the same fiber strand without interfering with each other. The GPON network is divided into three main components: the Optical Line Terminal (OLT), the Optical Network Unit (ONU), and the Optical Distribution Network (ODN).
The OLT serves as the main control and aggregation point of the GPON network. It receives data from the service provider's central office and sends it to the appropriate ONUs located at the customer's premises. The ONUs, also known as customer premises equipment, receive the data and distribute it to connected devices such as computers, phones, and smart home devices. The ODN consists of passive splitters and fiber optic cables that connect the OLT to the ONUs, allowing for efficient data transmission.
Benefits of GPON
GPON offers numerous benefits over traditional copper-based networks and other fiber optic technologies. Here are some key advantages of GPON:
1. High Speeds: GPON provides gigabit speeds, allowing for fast downloads, uploads, and streaming.
2. Reliability: Fiber optic cables used in GPON are highly resistant to interference and provide a more stable connection compared to copper cables.
3. Scalability: GPON networks can easily accommodate a large number of users, making them ideal for densely populated areas.
4. Cost-effective: GPON requires fewer cables and equipment compared to other network technologies, resulting in lower installation and maintenance costs for service providers.
5. Future-proof: GPON infrastructure has the capacity to handle increasing data demands, ensuring its longevity in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
GPON vs. other network technologies
GPON vs. Ethernet
GPON and Ethernet are both widely used network technologies, but they have some key differences.
GPON is a passive network, meaning it does not require any active electronic components at the user end. This makes GPON more cost-effective to deploy and maintain. Ethernet, on the other hand, requires active network switches and routers at both ends, which can increase costs.
In terms of bandwidth, GPON offers higher speeds compared to traditional Ethernet connections. GPON can provide symmetrical speeds of up to 1 Gbps for both uploading and downloading, whereas Ethernet speeds can vary depending on the type of cable and network infrastructure in place.
However, Ethernet has the advantage of being compatible with existing network infrastructure, making it easier to integrate into an already established network. GPON requires dedicated fiber optic cables and equipment, which may require additional installation and upgrades.
GPON vs. DSL
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is another popular technology for delivering internet services, but it differs from GPON in several aspects.
One significant difference is the medium through which data is transmitted. GPON uses fiber optic cables, which can transmit data over long distances without degradation or signal loss. DSL, on the other hand, uses existing copper telephone lines, which may limit the maximum speeds and distance coverage.
GPON also offers higher speeds compared to DSL. While DSL speeds can vary depending on the distance between the customer premises and the telephone exchange, GPON can provide consistent gigabit speeds regardless of distance.
Furthermore, GPON technology is more scalable and capable of handling multiple services simultaneously. DSL networks may face limitations in terms of bandwidth and capacity, especially in areas with high user demand.
In summary, GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, a high-speed telecommunications network that uses fiber optic cables. It offers numerous benefits such as high speeds, reliability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. GPON differs from other network technologies such as Ethernet and DSL in terms of deployment cost, bandwidth, and scalability. With its ability to provide fast and reliable connectivity, GPON plays a vital role in meeting the ever-increasing demands of modern communication.
Key Takeaways: What does GPON stand for?
- GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network.
- It is a type of fiber optic technology that allows for high-speed internet connections.
- GPON uses a single fiber optic cable to transmit data to multiple users.
- It provides symmetrical speeds, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same.
- GPON is widely used in telecommunications networks to deliver internet, TV, and phone services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about GPON:
What is GPON and what does it stand for?
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It is a type of fiber optic communication technology that enables the transmission of data, voice, and video signals over a single optical fiber. GPON utilizes a passive optical network architecture, which means it does not require active components like repeaters or amplifiers to transmit signals over long distances.
GPON is commonly used in telecommunication networks to provide high-speed internet access to residential and business customers. It offers higher bandwidth, greater reach, and increased scalability compared to traditional copper-based technologies.
How does GPON work?
GPON works by using a single optical fiber to transmit both downstream and upstream data. It uses a process called wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) to separate the data into different channels, allowing simultaneous transmission in both directions.
In a GPON network, the central office (CO) serves as the main hub and is connected to multiple optical network terminals (ONTs) located at the customer premises. The CO sends data to the ONTs using different wavelengths of light, and the ONTs send data back to the CO using another set of wavelengths. This bidirectional communication allows for high-speed data transfer and enables services like internet access, voice calling, and video streaming.
What are the advantages of GPON?
GPON offers several advantages over traditional copper-based technologies:
1. High-speed internet: GPON provides symmetrical upload and download speeds, allowing for fast and reliable internet access.
2. Increased bandwidth: With GPON, more data can be transmitted simultaneously, accommodating the growing demand for bandwidth-intensive applications and services.
3. Longer reach: GPON can transmit signals over longer distances without the need for repeaters or amplifiers, reducing infrastructure costs and simplifying network deployment.
4. Scalability: GPON networks can be easily expanded to accommodate more users and services, making it a future-proof solution for evolving communication needs.
What are the limitations of GPON?
While GPON offers many benefits, it does have some limitations:
1. Fiber availability: GPON requires a fiber optic infrastructure, which may not be available in all areas. This can limit its deployment to regions with existing fiber networks.
2. Upfront costs: Building GPON networks requires significant investment in fiber optic cables, ONTs, and other equipment. This upfront cost can be a barrier to adoption, especially for small-scale deployments.
3. Signal loss: Optical signals can experience attenuation (signal loss) as they travel through the fiber. This can result in lower signal quality and reduced transmission distances.
4. Power dependency: GPON ONTs require power to function, so in the event of a power outage, the services provided by the network may be disrupted.
What are some common applications of GPON?
GPON is widely used in various applications, including:
1. Residential internet: GPON is commonly used to provide high-speed internet access to homes, offering faster speeds and greater bandwidth than traditional copper-based technologies.
2. Business connectivity: GPON enables reliable and scalable connectivity for businesses, supporting multiple users and bandwidth-intensive applications.
3. IPTV and video streaming: GPON networks can deliver high-quality video content, making them suitable for IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) services and video streaming platforms.
4. Telecommunications networks: GPON is extensively used in telecommunication networks to connect infrastructure, provide fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) services, and offer high-speed internet access to customers.
Summary
So, to sum it all up, GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It's a technology that uses fiber optic cables to provide high-speed internet and other communication services. GPON allows data to be transmitted over long distances without losing speed or quality. It's a more efficient and reliable way to connect to the internet and enjoy faster downloads, streaming, and online gaming. With GPON, you can experience the benefits of fiber optics right in your own home.
In conclusion, GPON is an important technology that brings fast and reliable internet to people. It's a really cool way to stay connected and enjoy all the things the internet has to offer. So, whether you're browsing the web, watching videos, or chatting with friends, GPON will make your online experience much smoother and more enjoyable.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote