
What Are The Challenges In Securing Smart Cities?"
When it comes to smart cities, there's an exciting future ahead, but there are also a few challenges that need to be addressed. So, what are the challenges in securing smart cities? Let's find out!
In today's world, where technology is becoming more integrated into our daily lives, smart cities offer a glimpse into the future of urban living. However, with all the benefits that smart cities bring, such as increased efficiency and improved quality of life, there are also concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy.
One of the key challenges in securing smart cities is the sheer amount of data that is generated and collected from various sources. With sensors, cameras, and connected devices scattered throughout the city, there is a constant stream of data that needs to be collected, analyzed, and protected. This presents a significant challenge in terms of securing this data and ensuring its integrity.
Overall, securing smart cities is a complex task that requires collaboration between government bodies, technology companies, and citizens themselves. By addressing the challenges of cybersecurity and data privacy, we can create a safer and more resilient future for our smart cities. So, let's dive in and explore these challenges in more detail!
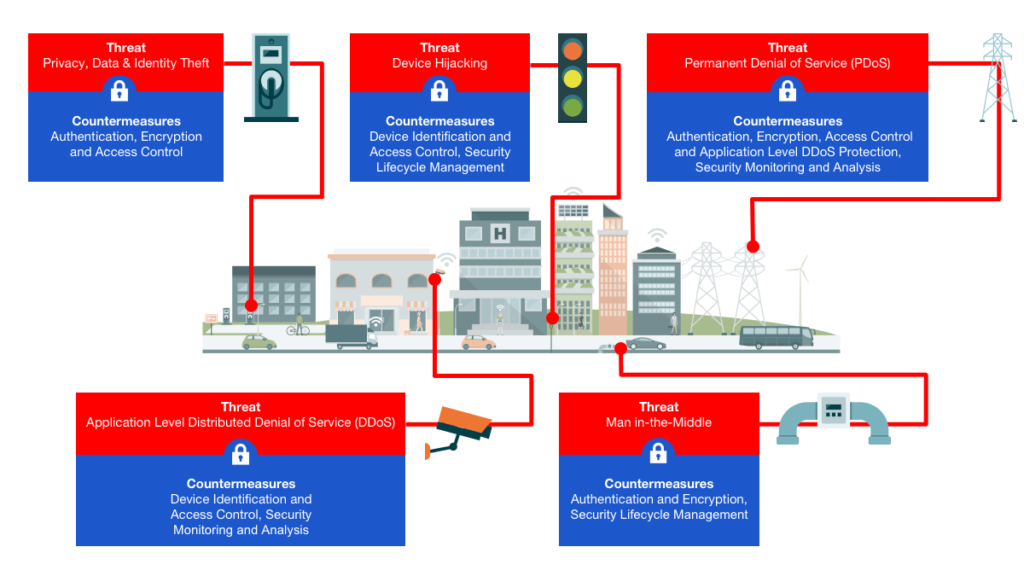
Challenges in Securing Smart Cities: Protecting the Future
Smart cities are destined to transform the way we live, work, and interact. With the promise of increased efficiency, sustainability, and convenience, these technologically advanced urban centers rely heavily on interconnected networks and data-driven systems. However, as the world becomes more digitally connected, so do the risks associated with cybersecurity and data breaches. In this article, we will dive into the fascinating world of smart cities and explore the challenges they face when it comes to securing their infrastructure and ensuring the safety of their citizens.
1. Vulnerabilities in IoT Devices
At the heart of smart cities lies the Internet of Things (IoT) - a vast network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data. While IoT devices are key to the functionality and efficiency of smart cities, they also present significant security challenges. Many of these devices are produced by different manufacturers, resulting in a lack of standardized security protocols. This makes them susceptible to attacks by hackers who can exploit vulnerabilities in the device's software or gain unauthorized access to the network.
Furthermore, the large-scale deployment of IoT devices in smart cities increases the attack surface and creates a web of interconnected weak points. A security breach in one device could potentially compromise the entire network, leading to severe consequences ranging from privacy breaches to disruptions in critical infrastructure.
Solutions to address these vulnerabilities include implementing stronger authentication mechanisms, regularly updating software and firmware, and establishing industry-wide security standards. Additionally, raising awareness among manufacturers, developers, and users about the potential risks is crucial to ensure a more secure IoT ecosystem.
2. Protecting Data Privacy
Smart cities thrive on the vast amount of data collected from sensors, cameras, and various other sources. This data is used to optimize services, enhance citizen experiences, and improve urban planning. However, the collection and usage of this data raise legitimate concerns about privacy and data protection.
Unauthorized access to sensitive data can result in identity theft, surveillance, and even blackmail. Smart cities must take robust measures to protect the privacy of their citizens and ensure that data is collected, stored, and managed securely. This involves implementing strong encryption measures, anonymizing data, and establishing strict access controls.
Furthermore, transparency and accountability are essential in building trust between the city authorities and its citizens. Smart cities should provide clear information on what data is being collected, how it is being used, and offer individuals the ability to consent or opt-out of data collection.
3. Ensuring Critical Infrastructure Security
Smart cities rely heavily on critical infrastructure systems such as power grids, water supply networks, transportation systems, and communication networks. These systems are highly interconnected and often interdependent, making them an attractive target for cybercriminals seeking to disrupt city operations.
A successful attack on critical infrastructure can have devastating consequences, ranging from financial losses to endangering human lives. To ensure the security of these systems, smart cities must adopt a multi-layered approach that includes perimeter security, continuous monitoring, and incident response plans.
Regular vulnerability assessments, threat modeling, and penetration testing can help identify weaknesses in the infrastructure and address them proactively. Collaborative efforts between city authorities, infrastructure operators, and cybersecurity experts are crucial in establishing a robust security framework to protect critical systems.
4. Securing Communication Networks
Communication networks form the backbone of any smart city, facilitating the seamless flow of data and enabling real-time decision-making. However, these networks are not immune to security risks. From cellular networks to Wi-Fi connectivity, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the communication infrastructure is vital.
An unsecured communication network can lead to unauthorized access, data manipulation, and even the disruption of essential services. Smart cities must implement robust encryption protocols, secure authentication mechanisms, and intrusion detection systems to protect their communication networks from cyberthreats.
Moreover, raising awareness among citizens about the importance of secure Wi-Fi connections and the potential risks of public Wi-Fi networks is crucial to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
5. Addressing the Insider Threat
While external cybersecurity threats often take the spotlight, the insider threat can be equally damaging to smart cities. Insiders, including employees, contractors, and service providers, have privileged access to critical systems and data, making them potential sources of cybersecurity breaches.
Smart cities need stringent access control mechanisms to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Regular monitoring and auditing of activities within the city's network can help detect any abnormal behavior or suspicious activity.
Educating and training employees on cybersecurity best practices and the potential consequences of insider threats is essential to create a culture of security within smart cities.
6. Managing Legacy Systems
Many smart cities are built on existing infrastructure that has been adapted to incorporate new technologies. These legacy systems often come with outdated software and cybersecurity vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers.
Managing and securing legacy systems poses unique challenges due to the limited support and compatibility issues. Smart cities must prioritize the identification and mitigation of vulnerabilities in these systems, implementing robust security controls and conducting regular updates or replacements when necessary.
Additionally, designing future smart cities with scalability, upgradability, and security in mind can help minimize the risks associated with legacy systems.
7. Developing Collaboration & Information Sharing
No single entity can tackle the challenges of securing smart cities alone. Collaboration and information sharing among cities, technology vendors, cybersecurity firms, and researchers are vital for staying ahead of emerging threats and finding innovative solutions.
Establishing public-private partnerships can facilitate the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and resources to enhance cybersecurity in smart cities. Sharing information about emerging cyber threats and best practices can help cities proactively address potential risks.
Furthermore, collaboration with academia and research institutions can fuel the development of new techniques, tools, and frameworks to secure smart cities effectively.
The Future Holds Promises and Challenges
As smart cities continue to evolve, so do the challenges in securing them. The benefits of these technologically advanced urban centers are undeniable, but without robust cybersecurity measures in place, the risks can outweigh the rewards. By addressing vulnerabilities in IoT devices, protecting data privacy, securing critical infrastructure, ensuring communication network security, addressing the insider threat, managing legacy systems, and fostering collaboration, smart cities can navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity and create a safer, more efficient urban environment for their citizens.
Key Takeaways: What Are the Challenges in Securing Smart Cities?
- Smart cities face multiple security challenges due to interconnected networks and devices.
- Protecting data and privacy is a major concern in securing smart cities.
- Cyberattacks on critical infrastructure pose a significant threat to smart cities.
- Securing IoT devices and networks is crucial for the overall security of smart cities.
- Collaboration between stakeholders, including government, industry, and citizens, is necessary to address the security challenges in smart cities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on the challenges facing smart cities when it comes to security. Here, we address common questions and provide insightful answers to help you understand the complexities involved. Let's dive in!
1. What potential security challenges do smart cities face?
In the fast-paced world of smart cities, security challenges are ever-present. One major concern is the vulnerability of interconnected devices and systems. As more devices are connected, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Additionally, ensuring the privacy of citizens' data poses a significant challenge, as smart cities rely on collecting and analyzing massive amounts of data for various services. Overcoming these challenges requires robust cybersecurity measures, privacy protections, and effective data management protocols.
Furthermore, as smart cities heavily rely on technology, there's an increased risk of infrastructure vulnerabilities. Ensuring the security of critical infrastructures like transportation systems and power grids becomes crucial to maintaining the smooth operation of these cities. Mitigating these vulnerabilities demands comprehensive risk assessments, strong security protocols, and constant monitoring and updates.
2. How can smart cities tackle the issue of cybersecurity?
Smart cities can address cybersecurity challenges through proactive measures. First, implementing strong encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication helps secure communication and access to interconnected devices. This makes it harder for hackers to intercept sensitive data or gain unauthorized access.
Moreover, fostering collaborative efforts between city authorities, IT professionals, and cybersecurity experts is crucial. This collaboration can lead to the development of robust cybersecurity frameworks and practices specifically tailored to smart city environments. Training programs and public awareness campaigns can also play a vital role in educating citizens about online security best practices.
3. What steps can be taken to protect citizen data in smart cities?
Protecting citizen data is a top priority for smart cities. An essential step is implementing strong data protection measures, such as end-to-end encryption, to safeguard personal information from malicious attacks. Additionally, establishing stringent data access controls ensures that only authorized personnel can view and handle sensitive data.
Transparency is another key aspect. Providing clear guidelines on data collection, usage, and storage practices helps build trust with citizens. Smart cities should also prioritize complying with relevant data protection regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and regularly audit their data management practices to identify and rectify any potential vulnerabilities or weaknesses.
4. How can smart cities enhance the security of critical infrastructures?
To enhance the security of critical infrastructures in smart cities, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. This includes robust physical security measures, such as surveillance cameras and access control systems, to monitor and control access to critical facilities. Regular maintenance and software updates are essential to address any vulnerabilities promptly.
Adopting a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines clear protocols in the event of an attack or disruption is vital. Regular drills and simulations can help identify weaknesses and improve response times. Additionally, implementing advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning can enhance threat detection and allow for real-time monitoring of critical infrastructures, enabling swift action when necessary.
5. How can public-private partnerships contribute to the security of smart cities?
Public-private partnerships play a crucial role in securing smart cities. By combining resources, expertise, and knowledge, these partnerships can drive innovation and develop effective security solutions. Private companies can offer advanced technologies and expertise, while public entities provide the necessary regulatory frameworks and access to infrastructure.
Collaborations also enable information sharing between the public and private sectors, aiding in early threat detection and prevention. By pooling their resources, public and private entities can work together to address security challenges, develop robust security standards, and foster a safer environment for everyone in smart cities.
Smart Cities Explained In 101 Seconds
Summary
Securing smart cities is a big challenge because there are many risks involved. One key challenge is the large number of connected devices, which creates more entry points for hackers to exploit. Another challenge is the lack of standard security protocols, making it difficult to ensure that all devices are properly protected. Additionally, smart city infrastructure is vulnerable to physical attacks, such as hacking into traffic systems or power grids. It's important to address these challenges in order to safeguard the privacy and security of residents in smart cities.
In conclusion, securing smart cities requires addressing the risks associated with the large number of connected devices, establishing standard security protocols, and protecting against physical attacks. By doing so, we can ensure that smart cities remain safe and secure places to live in.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote