
How Is GPON Different From DSL?
Looking to learn about the differences between GPON and DSL? Well, you're in the right place!
When it comes to internet connections, GPON and DSL are two popular options, but they have some distinct characteristics.
In this article, we'll explore how GPON, which stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, differs from DSL, or Digital Subscriber Line. So, let's dive right in and unravel the mysteries of these two technologies!
Curious about the differences between GPON and DSL? Both technologies are used for internet connections, but they have some key distinctions. GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, delivers faster speeds and greater bandwidth compared to DSL, which relies on copper phone lines. Additionally, GPON provides symmetrical upload and download speeds, while DSL offers higher download speeds but lower upload speeds. GPON is also more robust and less affected by distance limitations. Keep exploring to uncover more intriguing contrasts!
How is GPON different from DSL?
When it comes to internet connectivity, there are numerous options available, each with its own unique features and advantages. Two popular choices are GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) and DSL (Digital Subscriber Line). While both of these technologies provide internet access, they differ in several key aspects. In this article, we will explore the differences between GPON and DSL, shedding light on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
1. Technology
GPON and DSL are based on different technologies that determine their efficiency and performance. GPON utilizes fiber optic cables to transmit data using light signals, allowing for faster and more reliable internet connectivity. DSL, on the other hand, uses copper telephone lines to transmit data through electrical signals. The reliance on copper infrastructure in DSL can result in slower internet speeds and reduced reliability compared to GPON. Additionally, GPON technology has a higher capacity for bandwidth, enabling it to support more users simultaneously and accommodate advanced applications requiring high-speed connections.
Moreover, GPON technology is capable of offering symmetrical upload and download speeds, meaning the speed for data transmission is the same in both directions. DSL, on the other hand, generally provides asymmetrical speeds, with slower upload speeds compared to download speeds. This can impact activities such as video conferencing, online gaming, and cloud storage, where high upload speeds are essential.
2. Speed and Bandwidth
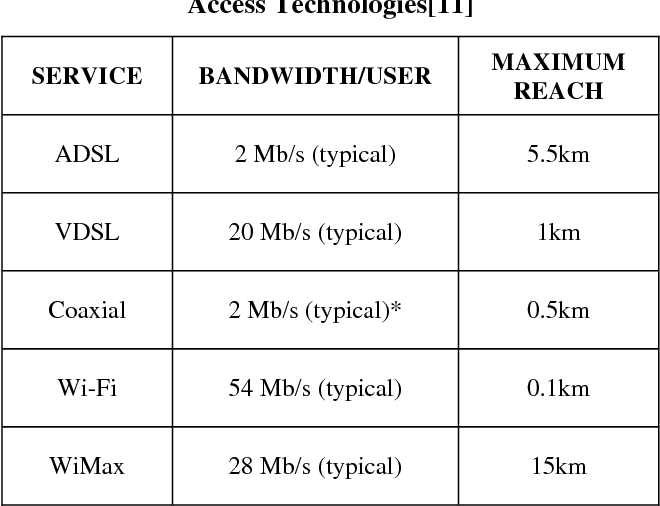
One of the significant differences between GPON and DSL is the speed and bandwidth they offer. GPON, being based on fiber optic technology, provides significantly higher speeds compared to DSL. While DSL speeds can vary depending on the distance from the exchange, GPON consistently offers faster downloads and uploads, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks such as streaming high-definition video, online gaming, and large file transfers.
Furthermore, GPON can deliver symmetrical speeds, typically ranging from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps (Gigabits per second) for both downloads and uploads. In contrast, DSL speeds usually range from 1 Mbps to 100 Mbps for downloads and have considerably slower upload speeds, often limited to a few Mbps. This discrepancy in speed and bandwidth makes GPON a more reliable and efficient choice for users who require fast and symmetrical internet connections.
3. Distance Limitations
Another key difference between GPON and DSL is the distance limitations they impose. GPON, being fiber-based, can support longer distances between the service provider's network and the user's premises without any significant loss in the quality of the connection. Fiber optic cables can transmit data over much longer distances compared to copper cables used in DSL. This allows for greater flexibility in terms of geographical coverage and enables service providers to reach customers in remote areas.
DSL, on the other hand, is limited by the physical length of the copper cables. As the distance increases between the user's location and the exchange, the signal quality deteriorates, resulting in slower internet speeds. Users situated far from the exchange may experience noticeably slower speeds and a less stable connection. This limitation makes DSL less suitable for users in rural or remote areas where the telecommunications infrastructure is not as well-developed.
4. Reliability and Security
When it comes to reliability and security, GPON holds an advantage over DSL. Fiber optic cables used in GPON are immune to electromagnetic interference, making the connection more stable and less susceptible to interruptions. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with high levels of electrical noise or environments prone to interference.
In terms of security, GPON offers enhanced privacy compared to DSL. Fiber optic cables do not emit any radiation or signals that can be easily intercepted, providing a higher level of security for data transmission. In contrast, DSL signals can be vulnerable to eavesdropping and hacking attempts, especially over longer distances where the signal strength is weaker.
5. Availability and Installation
One aspect to consider when choosing between GPON and DSL is their availability and installation requirements. GPON, being a relatively newer technology, might not be available in all areas. Its deployment requires the laying of fiber optic cables, which can be costly and time-consuming. As a result, GPON is typically found in urban and densely populated areas where the investment is economically justified.
DSL, on the other hand, has broader availability since it utilizes existing copper telephone lines. This makes DSL more accessible in remote and rural areas where fiber optic infrastructure might not be present. Moreover, the installation process for DSL is generally easier and faster compared to GPON, as it only requires connecting the modem to the telephone line. However, it is important to note that the proximity to the telephone exchange can affect the quality and speed of the DSL connection.
Benefits of GPON over DSL
GPON offers several key benefits over DSL, making it a preferable choice for many users:
- Unmatched speed and bandwidth capabilities
- Symmetrical upload and download speeds
- Higher reliability and stability
- Enhanced security and privacy
- Potential for future scalability
Cost Comparison
An important aspect to consider when choosing between GPON and DSL is the cost. While GPON may have higher initial installation costs, it typically provides better long-term value due to its superior performance, reliability, and scalability. DSL, despite its lower installation costs, may require frequent maintenance and upgrades to keep up with increasing bandwidth demands. Therefore, users should weigh the initial expenses against the long-term benefits to make an informed decision.
Tips for Choosing the Right Technology
When deciding between GPON and DSL, it is essential to consider various factors to determine which technology aligns best with your specific needs:
- Understand your internet requirements - Consider the types of activities you engage in online and the amount of bandwidth you need.
- Check availability - Determine whether GPON or DSL is available in your area to narrow down your options.
- Consider future scalability - Assess whether the technology can accommodate your future needs, such as increased usage or new applications.
- Evaluate budget - Consider the costs associated with installation, monthly plans, and potential maintenance and upgrades.
- Seek professional advice - Consult with internet service providers or professionals to understand the pros and cons of each technology in your specific context.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPON and DSL offer different advantages and features when it comes to internet connectivity. GPON provides faster speeds, higher bandwidth, greater reliability, enhanced security, and the potential for scalability. On the other hand, DSL is more widely available, requires less installation effort, and might be more cost-effective for some users. Understanding your internet requirements, checking availability, considering future scalability, evaluating your budget, and seeking professional advice are all crucial factors in choosing the right technology for your internet needs.
Key Takeaways: How is GPON different from DSL?
- GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, while DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line.
- GPON uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data at high speeds, while DSL uses copper telephone lines.
- GPON offers faster download and upload speeds compared to DSL.
- DSL connections have a limited range, while GPON can cover longer distances.
- GPON requires special equipment and installation, whereas DSL can use existing telephone infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
Want to know how GPON is different from DSL? Check out these common questions and answers.
1. What is GPON and how does it differ from DSL?
GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is a type of fiber optic technology that provides high-speed internet connectivity. It uses optical cables to transmit data at incredibly fast speeds, up to 2.5 gigabits per second. On the other hand, DSL, or Digital Subscriber Line, uses traditional copper telephone lines to transmit data, offering relatively slower speeds. The main difference between GPON and DSL lies in the medium used for data transmission - GPON uses fiber optics while DSL uses copper cables.
Fiber optic cables used in GPON provide superior data transmission capabilities compared to the copper cables used in DSL. GPON can deliver symmetrical speeds, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same, while DSL typically has faster download speeds but significantly slower upload speeds. Additionally, GPON doesn't suffer from signal degradation over long distances like DSL does, allowing for faster and more reliable internet connections, especially in remote areas.
2. Is there a difference in reliability between GPON and DSL?
Yes, there is a difference in reliability between GPON and DSL. GPON, being fiber optic-based, is highly reliable and less susceptible to interference or signal loss. Fiber optics are more resistant to electromagnetic interference, making GPON less prone to service disruptions caused by environmental factors like electrical noise or extreme weather conditions. DSL, on the other hand, can experience degradation in signal quality due to interference from nearby electrical devices or distance from the telephone exchange.
Another factor that affects reliability is the quality of the infrastructure. GPON networks are typically built with modern and robust fiber optic cables, ensuring a more stable and consistent connection. In contrast, DSL relies on aging copper telephone lines, which may suffer from degradation over time. Therefore, when it comes to reliability, GPON tends to outperform DSL, providing users with a more consistent and uninterrupted internet experience.
3. Which technology offers faster speeds, GPON or DSL?
GPON offers faster speeds compared to DSL. As mentioned earlier, GPON can provide speeds of up to 2.5 gigabits per second, while DSL generally offers speeds ranging from a few megabits per second to a maximum of around 100 megabits per second. The use of fiber optic cables in GPON allows for higher bandwidth, enabling faster data transmission both for downloads and uploads.
The speed difference between GPON and DSL becomes more prominent when considering distance. DSL speeds tend to degrade the further away a user is from the telephone exchange, while GPON maintains consistent high speeds regardless of distance. Therefore, if speed is an important factor for you, GPON is the better choice for achieving faster and more efficient internet connectivity.
4. Can I use my existing DSL modem for GPON?
No, you cannot use your existing DSL modem for GPON. GPON and DSL use different technologies and require distinct equipment for connectivity. GPON requires an Optical Network Terminal (ONT) installed at your premises, which is responsible for converting optical signals into usable internet data. In contrast, DSL modems are designed specifically for DSL connections and cannot function with GPON networks.
If you wish to switch from DSL to GPON, you will need to contact your service provider to install the necessary GPON equipment, including the ONT. This may involve a technician visit to your premises to ensure a smooth transition from DSL to GPON and to configure your network settings accordingly.
5. Is GPON available everywhere, or is it limited to specific areas?
GPON availability can vary depending on the location and the service providers in your area. While GPON has been rapidly expanding and becoming more accessible in recent years, it may still be more commonly available in urban areas compared to rural or remote regions. This is primarily due to the infrastructure required for GPON, as laying fiber optic cables can be more expensive and challenging in rural areas.
DSL, on the other hand, is more widely available as it utilizes existing telephone infrastructure. However, as demand for faster internet speeds and higher bandwidth increases, GPON deployment is expanding to reach a larger number of areas. If you're interested in GPON and want to check its availability in your area, it's best to contact local service providers or check their websites for coverage maps and availability in your specific location.
Summary
GPON and DSL are two different technologies used for internet connections. GPON provides faster speeds and more bandwidth compared to DSL.
GPON uses fiber optic cables, which transmit data using light, while DSL uses copper phone lines. Fiber optic cables can carry more data over longer distances without losing quality.
GPON is also more reliable because its signals are less affected by weather conditions and electrical interference. On the other hand, DSL can be influenced by distance from the provider, degrading the connection's speed and quality.
Overall, GPON is a better option for those who need faster internet speeds and want a more stable connection, while DSL may be suitable for those who are located closer to the provider and don't require the highest speeds.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote