
Are Other Options Better Than GPON?
Are you curious about whether other options are better than GPON? Well, my friend, you've come to the right place! In this article, we'll explore the world of fiber-optic internet and discover if there are alternatives that can outshine GPON.
Now, you might be wondering, "What exactly is GPON?" Great question! GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network and is a technology widely used for delivering high-speed internet to homes and businesses. But is it the best option out there? Let's find out!
Hold onto your hats because we're about to dive into the fascinating world of internet connectivity and uncover if GPON truly reigns supreme or if other options can give it a run for its money. Get ready to explore the possibilities beyond GPON!
Are Other Options Better than GPON in the World of Networking?
In today's interconnected world, high-speed internet is a necessity, and the choice of networking technologies plays a crucial role in delivering fast and reliable connections. One such technology is GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network), which has gained popularity for its ability to provide high bandwidth and reach. However, the question arises: are there other options that are better than GPON? In this article, we will explore various networking technologies and compare them with GPON to determine their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for different scenarios.
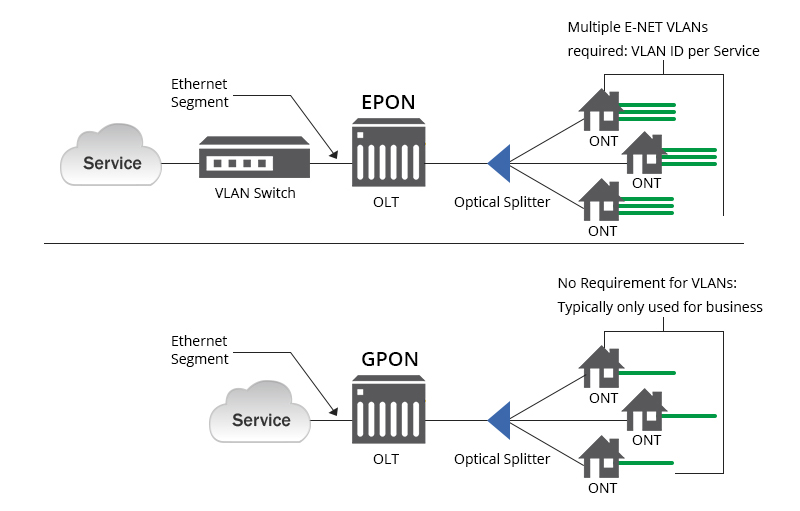
1) Ethernet: The Tried and Tested Solution
Ethernet, the most widely deployed networking technology, has been the go-to choice for both homes and businesses for years. It offers a reliable and robust connection, capable of delivering high-speed internet. Ethernet can be easily implemented using Cat6 or Cat6a cables, providing a simple and cost-effective solution. Moreover, Ethernet allows for easy integration with existing infrastructure, making it a flexible option for both small-scale and large-scale deployments.
Although Ethernet has many advantages, it does have limitations. The primary drawback is its distance limitations. Ethernet signals start to degrade after a certain distance, typically 100 meters, making it unsuitable for long-range connections without additional equipment such as switches or repeaters. Additionally, Ethernet requires physical cabling, which can be challenging to install in certain environments or require additional costs.
In summary, Ethernet is a reliable and versatile networking technology that excels in short- to medium-range connections. It offers high performance and flexibility but may not be the ideal choice for long-range or cost-sensitive deployments.
2) Wi-Fi 6: Empowering the Wireless Revolution
The advancement of wireless technology has revolutionized the way we connect to the internet. Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest and most advanced iteration of Wi-Fi technology. It brings significant improvements in speed, capacity, and performance, making it a compelling alternative to GPON for various scenarios.
One of Wi-Fi 6's notable advantages is its ability to support a large number of connected devices simultaneously. With increased bandwidth and improved efficiency, Wi-Fi 6 can handle the demands of modern homes and businesses, where numerous devices are connected at all times. Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 offers faster speeds and reduced latency, ensuring a seamless online experience for users.
Despite its advancements, Wi-Fi 6 does have limitations. The signal strength of Wi-Fi networks can degrade with distance, obstacles, or interference from other devices. In larger buildings or areas with many walls, Wi-Fi coverage may be compromised, leading to dead spots or reduced speeds. Moreover, Wi-Fi networks are susceptible to interference from neighboring networks, potentially impacting the overall performance.
In conclusion, Wi-Fi 6 is an excellent option for wireless connectivity, offering high speeds, capacity, and flexibility. It is best suited for environments with a high number of connected devices, but considerations should be made for signal strength and potential interference.
3) Fiber Optic: The Pinnacle of Speed and Reliability
When it comes to speed and reliability, fiber optic technology reigns supreme. Fiber optic networks use strands of glass or plastic to transmit data using light pulses, delivering exceptionally high bandwidth and minimal signal degradation. This makes fiber optic connections the ideal choice for scenarios where maximum performance is required.
One major advantage of fiber optic networks is their incredible speed. They can provide symmetrical speeds, meaning equal upload and download speeds, without any significant loss over long distances. This makes fiber optic connections perfect for demanding applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and large file transfers. Additionally, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring consistent performance even in densely populated areas.
However, fiber optic networks do come with a higher cost compared to other options. The installation and maintenance of fiber optic infrastructure can be expensive, making it less accessible for smaller companies or residential areas. Additionally, fiber optic connections require professional installation and specialized equipment, adding to the overall investment.
In summary, fiber optic networks are the pinnacle of speed and reliability, providing unmatched performance and future-proofing. They are best suited for applications that require ultra-fast speeds and can justify the higher cost of installation and maintenance.
Beyond GPON: Exploring Other Networking Technologies
4) Power-line Communication: Utilizing Existing Infrastructure
Power-line communication (PLC) is a networking technology that utilizes existing electrical power lines for data transmission. It enables the establishment of a network without the need for additional cables or wireless signals, making it a practical solution for specific scenarios.
PLC offers the advantage of easy installation, as it utilizes the electrical wiring already present in buildings. This can be convenient for retrofits or situations where installing new cables is challenging. Additionally, PLC connections can reach different rooms within a building, making them suitable for scenarios where Wi-Fi coverage is insufficient.
However, PLC has limitations that should be considered. The speed and reliability of PLC connections can be affected by factors such as distance, electrical noise, and the quality of the electrical wiring. Furthermore, power-line communication networks are generally slower compared to other options such as fiber optic or Ethernet, making them less suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications.
In conclusion, power-line communication is a viable alternative to GPON in specific situations where the use of existing electrical wiring is preferred. It offers convenient installation and coverage within buildings but may not provide the same level of performance as other technologies.
5) Cellular Networks: Wireless Connectivity on a Large Scale
Cellular networks, commonly known as 4G and soon to be 5G, allow wireless communication between devices using radio waves. They provide connectivity on a large scale, covering wide geographical areas and enabling mobile devices to connect to the internet without the need for physical cables.
The primary advantage of cellular networks is their widespread coverage. They allow for internet access even in remote locations or areas where other technologies are unavailable. Additionally, cellular networks provide mobility, allowing users to stay connected while on the move.
Despite their advantages, cellular networks have some limitations. The speed and reliability of cellular networks can vary depending on factors such as signal strength, network congestion, and the distance to cellular towers. In densely populated areas, network congestion can lead to reduced speeds and inconsistent performance. Moreover, cellular data plans often have data caps or limitations, making them less suitable for heavy data usage or bandwidth-intensive applications.
In summary, cellular networks are an excellent option for users who require internet connectivity on the go or in areas with limited infrastructure. They offer wide coverage and mobility benefits but may not provide the same level of performance or cost-effectiveness as other technologies for fixed locations.
6) Satellite Internet: Connecting the Unreachable
Satellite internet is a technology that utilizes communication satellites orbiting the Earth to provide internet connectivity. It is an ideal choice for areas where terrestrial connections, such as fiber optic or Ethernet, are unavailable or impractical to install.
One of the significant advantages of satellite internet is its wide coverage area. It can reach remote regions, rural areas, or even ships at sea, bridging the connectivity gap for those who would otherwise be left without internet access. Additionally, satellite internet can provide relatively fast speeds, making it suitable for various online activities.
However, satellite internet does have limitations that should be considered. Latency, the time it takes for data to travel to and from the satellite, can be higher compared to other technologies. This can result in slower response times, making it less suitable for real-time applications such as online gaming or video conferencing. Additionally, weather conditions can impact satellite signal quality, leading to potential disruptions or reduced speeds during severe weather events.
In conclusion, satellite internet is an excellent option for areas where other technologies are not feasible. It offers wide coverage and relatively fast speeds but may have higher latency and potential weather-related limitations.
The Verdict: Choosing the Right Option
7) Considerations and Suitability for Different Scenarios
When deciding whether other options are better than GPON, it is essential to consider the specific requirements and constraints of the given scenario. Each networking technology discussed in this article has its strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different situations.
Ethernet excels in providing reliable and cost-effective solutions for short- to medium-range connections, making it a solid choice for homes and businesses. Wi-Fi 6 offers wireless convenience and high capacity, making it ideal for environments with numerous connected devices. Fiber optic technology provides unmatched speed and reliability, making it perfect for demanding applications that require ultra-fast connections.
Power-line communication can utilize existing infrastructure and provide coverage within buildings, offering convenience in certain scenarios. Cellular networks offer wide coverage and mobility benefits, catering to users on the go or in remote locations. Satellite internet bridges the connectivity gap for areas where terrestrial connections are not feasible, but considerations should be made for latency and weather-related limitations.
In summary, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to whether other options are better than GPON. The choice depends on the specific requirements, budget, and constraints of each scenario. By carefully considering the strengths and weaknesses of each networking technology, the right option can be chosen to meet the unique needs of any situation.
Takeaway: Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various networking technologies is essential in making an informed decision. While GPON offers high bandwidth and reach, other options such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi 6, fiber optic, power-line communication, cellular networks, and satellite internet provide different advantages and limitations. By considering the specific requirements and constraints of a scenario, the right option can be chosen to deliver fast and reliable internet connectivity.
Key Takeaways: Are other options better than GPON?
- 1. Fiber optic technologies like XGS-PON and NG-PON2 offer higher bandwidth than GPON.
- 2. Ethernet-based solutions such as EPON and 10G-EPON provide better flexibility and scalability.
- 3. GPON is more cost-effective for typical residential and small business applications.
- 4. Other options may require higher upfront investment and specialized equipment.
- 5. The choice between GPON and other options depends on specific needs, budget, and growth plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ page, where we answer your questions about GPON and other options available. Discover which options may be better suited for your needs.
Question 1: What are some alternatives to GPON for broadband access?
Answer: While GPON is a popular choice, there are other options worth considering. One alternative is Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON), which offers high-speed internet access through optical fiber. Another option is Cable Modem, which utilizes existing cable TV infrastructure for broadband connectivity. Both EPON and Cable Modem can provide comparable speeds to GPON but may vary in terms of cost, availability, and overall performance.
Question 2: Are there any wireless alternatives to GPON for broadband access?
Answer: Yes, there are wireless options for broadband access that can be considered instead of GPON. One example is Fixed Wireless, which uses radio signals to provide high-speed internet connections. Another option is Satellite Internet, which utilizes satellites orbiting the Earth to deliver internet access. These wireless alternatives can be convenient in areas where physical infrastructure like cables or fibers are difficult to deploy. However, it's important to note that wireless solutions may be affected by factors such as signal strength, weather conditions, and distance from the provider's equipment.
Question 3: How does GPON compare to other options in terms of speed and reliability?
Answer: GPON is known for its high-speed capabilities and reliability. In terms of speed, GPON can provide symmetrical download and upload speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps. This makes it suitable for bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing. In terms of reliability, GPON's use of optical fiber makes it less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal loss. However, it's worth noting that other options like EPON, Cable Modem, Fixed Wireless, and Satellite Internet can also offer comparable speeds and reliability, albeit with potential variations depending on the specific technology and infrastructure in place.
Question 4: What factors should I consider when choosing between GPON and other options?
Answer: When choosing between GPON and alternative options, several factors should be considered. Firstly, availability plays a crucial role. Some areas may have limited or no access to certain technologies, making GPON or another option the only viable choice. Secondly, cost is an important consideration. Different options may vary in terms of installation costs, monthly fees, and equipment expenses. Additionally, the required speed and reliability for your specific needs should be taken into account. Finally, it's advisable to research and compare the customer reviews and feedback for each option to gauge the satisfaction levels of existing users.
Question 5: Can I switch from GPON to another option if I'm not satisfied with its performance?
Answer: In most cases, it is possible to switch from GPON to another broadband access option if you are not satisfied with its performance. However, the availability of alternatives may vary depending on your location. It's recommended to check with local internet service providers to determine the availability of other options in your area. Additionally, factors such as contractual obligations or early termination fees may apply, so it's important to review the terms and conditions of your current service agreement. Before making any decisions, consider researching and comparing the performance, cost, and reliability of the alternatives to determine the best fit for your needs.
GPON vs. EPON vs. XGS-PON - ProLabs Podcast Clip
Summary
So, to sum it all up, GPON is a widely-used internet technology. It offers fast speeds, high bandwidth, and supports multiple connections. However, there are other options to consider.
One alternative is Ethernet, which is faster and more flexible, but may be more expensive. Another option is wireless internet, which is convenient but can be affected by signal interference and limited range. Ultimately, the choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote