
Are GPON Networks Vulnerable To Interference?
Are GPON networks vulnerable to interference? Let's dive into the fascinating world of GPON networks and find out! Picture this: you're streaming your favorite show, but suddenly, the video starts buffering. Frustrating, right? Well, it could be due to interference in the GPON network. But what exactly is GPON, and how does interference affect it? Stick around as we explore this intriguing topic!
If you're wondering what GPON is, it stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. Sounds fancy, doesn't it? Well, GPON is a technology that uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data at incredible speeds. It's like having a superhighway for information, enabling faster internet connections and reliable communication. But here's the catch – just like any other network, GPON systems aren't immune to interference.
Now, when we talk about interference, we're referring to anything that disrupts the smooth flow of data in a GPON network. It could be a physical obstacle like a tree or a building blocking the signal, or it could be something called electromagnetic interference. This type of interference occurs when other electronic devices emit waves that interfere with the GPON signals, leading to reduced performance and slower internet speeds.
So, are GPON networks vulnerable to interference? The answer is yes, but the good news is that there are measures in place to mitigate these issues. Service providers and network engineers design GPON networks with tools and technologies that minimize interference, ensuring a seamless connection for users. So, stay tuned as we explore ways to overcome the challenges posed by interference in GPON networks!
GPON networks are generally resistant to interference due to various built-in security measures. With robust encryption protocols and dedicated wavelengths, GPON networks offer high levels of data transmission security. However, external factors like power surges or physical damage to the optical fiber can potentially disrupt network performance. Implementing proper installation practices, surge protection mechanisms, and regular maintenance can help mitigate these risks. By following industry best practices, GPON networks can maintain stable and secure connectivity, ensuring minimal susceptibility to interference.
Are GPON Networks Vulnerable to Interference?
GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) has become increasingly popular in recent years as a cost-effective solution for delivering high-speed internet access to both residential and business users. However, as with any technology, there are potential vulnerabilities that need to be considered. One such concern is the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference. In this article, we will delve into the details of GPON networks and explore the issue of interference to determine if there is cause for concern.
How GPON Networks Work
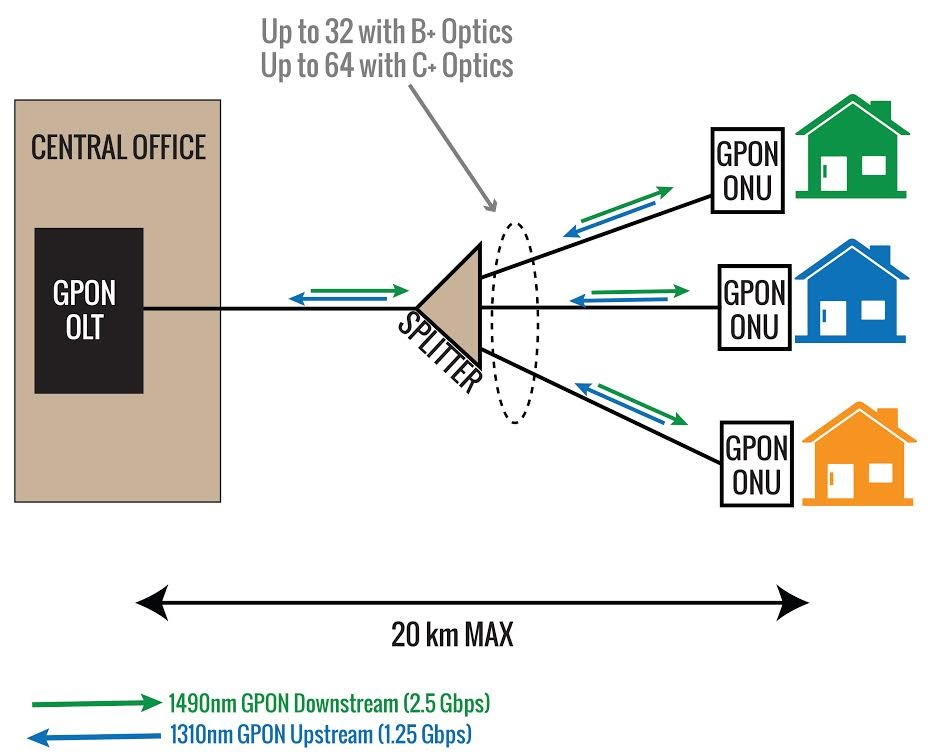
Before diving into the topic of interference, let's first understand how GPON networks function. GPON is a fiber-optic network architecture that leverages passive optical splitters to distribute signals to multiple endpoints. The network operates by dividing the available bandwidth into downstream and upstream channels. The downstream channel delivers data from the service provider to the end-user, while the upstream channel carries user-generated data back to the provider. This bidirectional communication allows for high-speed internet access and various services such as voice, video, and data.
GPON networks utilize time division multiplexing (TDM) to distribute the available bandwidth among multiple users. The optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's end coordinates the data transmission, ensuring efficient allocation of resources. Optical network terminals (ONTs) installed at the user's premises serve as interface points to connect devices such as modems, routers, or computers to the network.
Now that we have a basic understanding of how GPON networks operate, let's explore the potential vulnerabilities that these networks may face in terms of interference.
The Possibility of Electrical Interference
One potential source of interference in GPON networks is electrical interference. Electrical interference can arise when GPON cables are in close proximity to sources of electrical noise, such as power lines or electrical equipment. This interference can impact the performance of the network, leading to degraded signal quality and reduced throughput.
GPON networks typically use optical fibers for long-distance transmission. These fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI). However, the ONTs and other network equipment that connect to the fibers may be susceptible to electrical interference. As a precautionary measure, it is advisable to ensure proper grounding and shielding of the network equipment to minimize the potential for electrical interference.
In addition, during the installation or maintenance of GPON networks, care should be taken to avoid routing the cables or equipment in close proximity to sources of electrical noise. Proper cable management and separation from power lines can go a long way in reducing the chances of electrical interference affecting the network.
Potential Optical Interference Issues
While optical fibers used in GPON networks are immune to electrical interference, they are not completely impervious to all forms of interference. An issue known as optical beat interference (OBI) can occur when multiple optical signals in the network interfere with one another. OBI can arise when multiple ONTs transmit or receive data simultaneously, resulting in overlapping signals.
To mitigate OBI, GPON networks employ a time-division multiple access (TDMA) mechanism, where each ONT is given a specific time slot for transmission. This time-division-based scheduling prevents simultaneous transmission and reduces the chances of OBI. Additionally, signal processing techniques such as wavelength modulation and optical filtering help minimize OBI and ensure reliable data transmission.
Another optical interference issue that can affect GPON networks is optical crosstalk. Optical crosstalk occurs when signals intended for a specific ONT leak onto adjacent fibers, causing unintended signal interference. This can result in signal degradation and data errors. To combat optical crosstalk, GPON networks utilize technologies such as wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) and optical isolation to ensure that signals only reach their intended destinations.
Factors That Can Exacerbate Interference
While GPON networks are designed with built-in mechanisms to mitigate interference, certain factors can exacerbate the potential for interference. One such factor is the distance between the ONT and the OLT. As the distance increases, the signal attenuation increases, making the network more susceptible to interference.
The quality of the fiber optic cables and connectors used in the network infrastructure also plays a crucial role. Poorly maintained or damaged cables can introduce additional signal loss and increase the susceptibility to interference. It is essential to regularly inspect and replace damaged cables to ensure optimal network performance.
The environment in which GPON networks are deployed can also impact interference levels. For example, if they are situated in areas with heavy electrical equipment or industries that generate significant electromagnetic noise, the potential for interference may be higher. Proper planning and careful consideration of the deployment environment can help minimize interference risks.
Key Takeaways: Are GPON networks vulnerable to interference?
- GPON networks can be vulnerable to interference from various sources.
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby power sources or other devices can affect the performance of GPON networks.
- Physical obstructions like trees and buildings can cause signal degradation in GPON networks.
- Proper installation and maintenance can minimize the impact of interference on GPON networks.
- Network providers often employ techniques like shielding and signal amplification to combat interference in GPON networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Welcome to our FAQ section on GPON networks and interference. Here, we'll address some common questions regarding the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference. Read on to learn more!
1. How vulnerable are GPON networks to interference?
GPON networks, although generally robust, can be susceptible to interference in certain scenarios. Interference can be caused by various factors such as electromagnetic radiation, signal leakage, and neighboring networks operating on overlapping frequencies. While GPON systems are designed with measures to mitigate interference, it's necessary to ensure proper installation and maintenance to minimize its impact.
Regular testing and monitoring are crucial to identify and address any interference issues promptly. By employing best practices and adhering to industry standards, network operators can significantly reduce the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference.
2. What are some common sources of interference for GPON networks?
GPON networks can experience interference from a range of sources, including electrical equipment, wireless devices, nearby radio transmitters, and adjacent fiber optic cables. Outdated or faulty components and poorly shielded cables can also contribute to interference. Additionally, environmental factors such as power line proximity and radio frequency congestion can introduce interference into the network.
To mitigate interference, it's important to conduct a thorough assessment of potential sources, identify any problematic areas, and implement proper shielding techniques. Regular maintenance and inspections can help detect and address any new sources of interference that may arise.
3. Can weather conditions affect the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference?
Yes, certain weather conditions can impact the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference. For example, heavy rain or snowfall can cause signal attenuation due to moisture absorption by fiber optic cables. This can lead to decreased performance and potential service disruptions. Additionally, extreme temperature fluctuations can affect the stability and reliability of network equipment, potentially leading to interference issues.
To mitigate weather-related interference, GPON networks should be designed to withstand environmental conditions within specified operational limits. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help detect any weather-related issues promptly and allow for timely repairs or adjustments to minimize the impact on network performance.
4. How does GPON network design affect vulnerability to interference?
The design of GPON networks plays a crucial role in determining their vulnerability to interference. Proper planning and implementation of network architecture, such as adequate spacing between fiber cables and careful consideration of signal propagation characteristics, can help minimize interference. Additionally, the use of high-quality components and proper cable shielding can enhance network resilience.
Other factors that can influence vulnerability to interference include the number of active subscribers, quality of network equipment, and distance between the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and Optical Network Units (ONUs). By employing industry best practices and adhering to GPON design guidelines, network operators can optimize network performance and reduce the risk of interference.
5. How can network operators minimize interference in GPON networks?
To minimize interference in GPON networks, network operators should follow several key steps. These include conducting proper site surveys to identify potential sources of interference, implementing effective cable management and shielding techniques, and ensuring regular maintenance and inspections to detect and address interference issues promptly. Additionally, utilizing advanced network monitoring tools and techniques can help identify and resolve interference-related problems.
By staying up-to-date with industry standards, investing in high-quality network equipment, and training staff on best practices, network operators can minimize the vulnerability of GPON networks to interference. Ongoing monitoring and optimization efforts are essential to identify and mitigate any new sources of interference that may arise over time.
Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) Technology
Summary
GPON networks can be affected by interference that can slow down internet speeds and disrupt connectivity. This interference can come from various sources, such as neighboring networks or electronic devices in the vicinity.
To minimize interference, network providers use techniques like wavelength division multiplexing and signal processing algorithms. However, users can also help by placing their routers away from potential sources of interference and using Wi-Fi extenders to improve coverage. It's important to understand that while GPON networks are generally reliable, they can still be susceptible to interference, so it's important to take precautions to ensure a smooth and uninterrupted internet experience.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote