
Are GPON Networks Future-proof?
Are GPON networks future-proof? If you're wondering whether GPON networks have what it takes to stand the test of time, you've come to the right place! In this article, we'll explore the fascinating world of GPON networks and delve into whether they can keep up with the ever-evolving technological landscape. So, whether you're a tech enthusiast or just curious about the future of internet connectivity, let's dive in!
Picture this: you're streaming your favorite show, gaming with friends, and browsing the web all at once. It's a dream come true, right? Well, GPON networks make this dream a reality by delivering high-speed internet access straight to your home. But what exactly is GPON?
GPON, short for Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is a cutting-edge technology that uses fiber-optic cables to transmit data at lightning-fast speeds. It's like upgrading from a bicycle to a race car! With GPON, you can enjoy seamless video streaming, lag-free online gaming, and lightning-quick downloads. But here's the million-dollar question: will GPON networks be able to keep up with the demands of the future? Let's find out!
Join us as we explore the world of GPON networks, uncover their strengths and limitations, and discover whether they are future-proof. Get ready to embark on a thrilling journey through the future of internet connectivity. Let's zoom ahead and discover what lies ahead for GPON networks!
Are GPON Networks Future-Proof?
With the rapid advancement in technology and the ever-increasing demand for high-speed internet, it is crucial to consider the future-proofness of networking solutions. In this article, we will explore the topic of GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) networks and analyze whether they are future-proof. GPON networks have gained popularity in recent years due to their ability to provide high-speed internet access, but how well do they stand up against emerging technologies and evolving consumer needs? Let's delve into the details and find out.
Understanding GPON Networks: The Basics
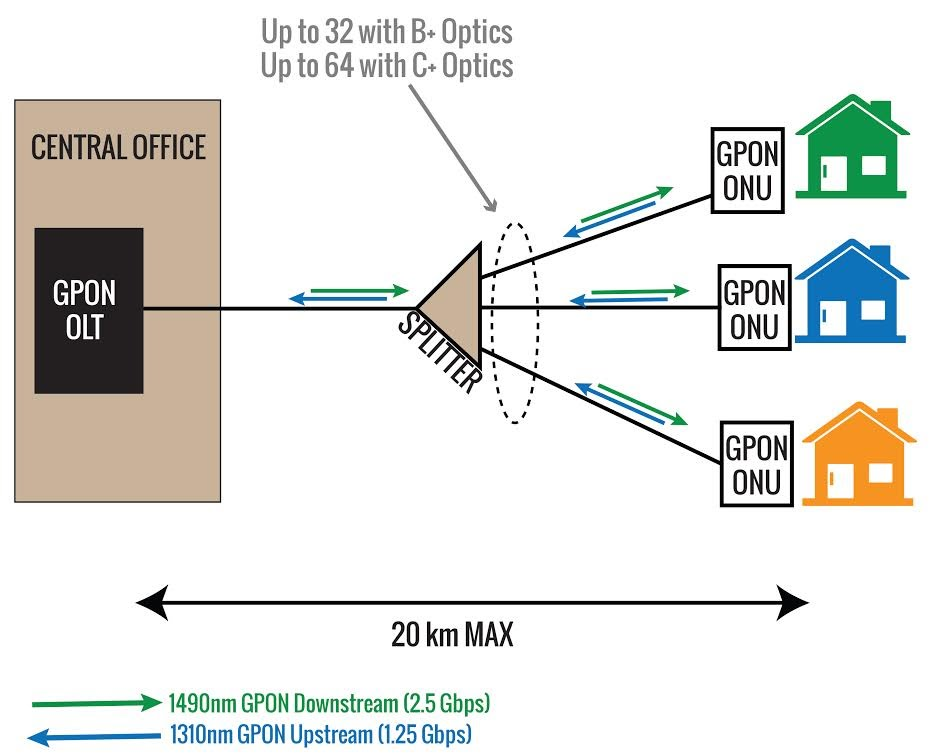
Before we dive into the future-proofness of GPON networks, let's first grasp the fundamentals. GPON is a fiber-optic communication technology that enables the transmission of data, voice, and video over a single optical fiber. It utilizes passive optical splitters to distribute the signal to multiple users, making it a cost-effective solution. GPON operates on an asynchronous time-division multiplexing (ATDM) mechanism, allowing for efficient utilization of available bandwidth.
One of the key advantages of GPON networks is their ability to deliver high-speed internet access. With downstream speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps and upstream speeds of up to 1.25 Gbps, GPON networks provide a significant boost in data transfer rates compared to traditional copper-based networks. This makes them ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications such as video streaming, online gaming, and cloud computing.
Furthermore, GPON networks offer a high degree of scalability, allowing service providers to easily expand their network capacity as demand increases. By adding more optical splitters and fiber connections, they can accommodate a larger number of subscribers without compromising performance.
The Evolution of Networking Technologies
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, it is important to consider how GPON networks stack up against emerging alternatives. One such technology is XGS-PON (10-Gigabit Symmetric Passive Optical Network), which offers symmetrical speeds of up to 10 Gbps. XGS-PON provides a future-proof solution for ultra-high-speed connectivity, surpassing the capabilities of GPON networks.
However, the transition from GPON to XGS-PON involves significant infrastructure upgrades and investments. Service providers need to replace optical network units (ONUs) and optical line terminals (OLTs) to migrate to XGS-PON. This can be a complex and costly process, making the future-proofness of GPON networks a relevant consideration.
It is worth noting that GPON networks still provide ample bandwidth for most residential and small-to-medium-sized business needs. The demand for ultra-fast internet speeds may vary depending on the specific requirements of each user. Therefore, while XGS-PON offers enhanced capabilities, the question of whether GPON networks are future-proof depends on individual needs and expectations.
The Benefits of GPON Networks
Despite the emergence of alternative technologies, GPON networks continue to offer numerous benefits that contribute to their future-proofness. Let's explore some of these advantages in detail.
1. High-Speed Connectivity:
GPON networks deliver impressive speeds that meet the needs of most users. The downstream and upstream speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps and 1.25 Gbps, respectively, allow for seamless video streaming, online gaming, and fast file downloads. For the majority of residential and small-to-medium-sized business users, GPON networks provide a future-proof solution.
2. Cost-Effectiveness:
GPON networks are an affordable alternative to other fiber optic technologies. Their use of passive components, such as splitters, reduces the need for active equipment at each user's location. This leads to lower installation and maintenance costs, making GPON networks an attractive option for service providers and end-users alike.
3. Scalability:
GPON networks can be easily scaled up to meet increasing demands. Service providers can add more optical splitters and fiber connections to expand their network capacity without significant disruptions. This scalability ensures that GPON networks can continue to serve a growing number of users without compromising performance or requiring costly infrastructure upgrades.
4. Reliability:
GPON networks offer high reliability due to the use of fiber optic cables, which are highly resistant to environmental factors such as electromagnetic interference and signal degradation. This ensures consistent and stable connectivity, minimizing downtime and providing a reliable internet experience.
5. Fiber Future-Proofness:
GPON networks are based on fiber optic technology, which is known for its future-proof characteristics. Fiber optic cables have a significantly higher capacity for data transmission compared to copper-based cables, making them well-suited for future advancements in technology and increasing bandwidth requirements. Adopting a GPON network lays the foundation for future upgrades to even faster fiber optic technologies.
GPON Networks vs. Alternatives: A Comparative Look
While GPON networks offer numerous benefits, it is essential to compare them with alternative networking technologies to assess their future-proofness. Let's explore how GPON networks fare against some notable alternatives.
GPON vs. DOCSIS 3.1:
DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) 3.1 is a technology that allows data transmission over existing cable TV systems. It offers high-speed internet access comparable to GPON networks. However, DOCSIS 3.1 relies on shared bandwidth, which can result in reduced speeds during peak usage periods. In contrast, GPON networks provide dedicated bandwidth to each user, ensuring consistent performance even during high-demand periods.
Additionally, GPON networks have a higher potential for future scalability as they are not limited by the existing cable infrastructure. This makes GPON networks a more future-proof option, particularly for areas where cable infrastructure is less developed or where higher speeds are desired.
GPON vs. 5G Wireless:
5G wireless technology promises incredibly fast and low-latency wireless connectivity. While 5G offers impressive speeds, it is subject to limitations such as signal propagation and coverage area. GPON networks, on the other hand, provide a reliable and consistent connection through dedicated fiber optic lines. This makes GPON networks a better choice for applications that require consistent high-speed connectivity, such as gaming, video streaming, and business applications.
However, it is worth noting that 5G wireless technology is rapidly evolving and may become a viable alternative to GPON networks in the future, especially in areas where fiber optic infrastructure is limited.
GPON vs. XGS-PON:
XGS-PON is a more advanced fiber optic technology that offers symmetrical speeds of up to 10 Gbps, surpassing the capabilities of GPON networks. However, as mentioned earlier, the transition from GPON to XGS-PON involves significant infrastructure upgrades and investments. In cases where ultra-high-speed connectivity is not an immediate requirement, GPON networks still provide a reliable and cost-effective solution.
Service providers should carefully assess their users' needs and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of transitioning to XGS-PON. For many, GPON networks continue to be a future-proof option that offers an excellent balance between speed, scalability, and cost.
GPON Networks: The Future Perspective
As we look towards the future of networking, it is clear that GPON networks have a vital role to play. While emerging technologies like XGS-PON and 5G wireless offer enhanced capabilities, GPON networks continue to provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for the majority of users.
The Key Takeaways:
- GPON networks deliver high-speed connectivity, making them suitable for most residential and small-to-medium-sized business needs.
- GPON networks are cost-effective due to their use of passive components and scalable for future expansion.
- GPON networks provide reliable and stable connectivity through the use of fiber optic cables, ensuring a future-proof foundation for advancements in technology.
- While alternative technologies like DOCSIS 3.1, 5G wireless, and XGS-PON offer their own advantages, GPON networks continue to be a practical and future-proof choice for many users.
So, are GPON networks future-proof? The answer lies in the specific needs and expectations of the users. For most users, GPON networks offer a reliable and cost-effective solution, providing ample bandwidth for current and foreseeable future requirements. As technology continues to evolve, the transition to more advanced networking technologies can be considered. However, GPON networks will likely remain a viable and future-proof option for years to come.
Key Takeaways: Are GPON Networks Future-Proof?
- GPON networks, which stand for Gigabit Passive Optical Networks, are designed to provide high-speed internet connections.
- GPON networks use fiber optic cables to transmit data, allowing for faster and more reliable speeds compared to traditional copper-based networks.
- While GPON networks offer impressive performance, it's essential to consider future advancements in technology.
- As technology continues to evolve, there may be other network options that offer even faster speeds and more advanced features.
- However, GPON networks are still a viable choice for many as they offer significant speed improvements over older network technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to the future of GPON networks, you may have some questions in mind. We've got you covered. Check out these commonly asked questions and their answers below.
1. What are GPON networks and why are they important?
GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) networks are a type of fiber optic network that deliver high-speed internet, television, and telephone services to homes and businesses. They use optical fibers to transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently. GPON networks are important because they provide reliable and ultra-fast internet connectivity, allowing users to stream high-definition videos, play online games, and connect multiple devices simultaneously without experiencing lag or slowdowns.
Additionally, GPON networks have a significant impact on the future of technology. As the demand for internet bandwidth continues to grow, GPON networks play a crucial role in meeting these demands and supporting technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), virtual reality (VR), and 4K/8K streaming. They provide the necessary infrastructure to ensure that our digital lifestyles can thrive.
2. Are GPON networks future-proof?
Yes, GPON networks are considered to be future-proof. Although there are newer technologies emerging, such as 10 Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (XG-PON), GPON networks still have a lot to offer in terms of speed and capacity. They can currently provide speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps (gigabits per second) for downstream and 1.25 Gbps for upstream, which is more than sufficient for most applications. Moreover, GPON networks have proven to be highly reliable and cost-effective, making them a viable choice for network providers.
Even as technology advances, GPON networks can still be upgraded to support higher speeds and increased bandwidth by implementing new technologies like NG-PON2 (Next-Generation Passive Optical Network 2). This allows network providers to adapt and evolve their infrastructure without compromising their existing GPON investments. Therefore, with ongoing updates and improvements, GPON networks have a promising future ahead.
3. Can GPON networks support increasing bandwidth demands?
Yes, GPON networks have the capability to support increasing bandwidth demands. As more and more devices and applications require fast and reliable internet connectivity, GPON networks can handle the growing demand for data transmission. With their fiber optic infrastructure, they are capable of providing high upload and download speeds, ensuring a seamless experience for users.
Furthermore, GPON networks are designed to be scalable. This means that as bandwidth requirements increase, network providers can upgrade the existing infrastructure to meet the demands. Upgrades can include deploying additional fiber optic cables or implementing newer technologies to boost network capacity. With the ability to adapt and grow, GPON networks are well-equipped to handle the evolving needs of users in the future.
4. Are there any drawbacks to GPON networks?
While GPON networks offer numerous advantages, there are a few drawbacks to consider. One potential limitation is the shared bandwidth. GPON networks distribute bandwidth among multiple users, which means that during peak usage times, speeds may be slightly lower. However, this is usually not noticeable for the average user, as GPON networks are designed to handle high data traffic efficiently.
Another consideration is the distance limitation. GPON networks have a maximum reach of around 20 kilometers, which can be a limitation in areas with dispersed population or remote locations. However, this can be alleviated by implementing additional optical line terminal (OLT) equipment or by using fiber-to-the-distribution-point (FTTdp) solutions for longer distances.
5. Are GPON networks cost-effective?
Yes, GPON networks are considered to be cost-effective. Compared to other technologies like Ethernet or cable, GPON infrastructure requires fewer cables and requires less power, resulting in lower installation and maintenance costs. The use of fiber optic cables in GPON networks also contributes to their cost-effectiveness, as they have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance compared to copper-based cables.
Additionally, GPON networks offer a high return on investment due to their scalability. Network providers can easily upgrade and expand the network capacity as needed, allowing them to adapt to the ever-increasing bandwidth demands without significant infrastructure overhauls. This flexibility and cost-efficiency make GPON networks an attractive choice for both network providers and end-users.
Summary
So, to sum it all up, GPON networks are a great choice for future-proofing our internet connections. They offer high speeds, are cost-effective, and can handle multiple services. However, there are some limitations around scalability and bandwidth allocation that need to be considered.
In conclusion, GPON networks are a solid option for now, but as technology continues to evolve, we may see even more advanced alternatives in the future. It's important for us to keep an eye on emerging trends and be ready to adapt as needed.
Recent Posts
- How Does GPON Improve Network Efficiency?
- What Are The Advantages Of GPON?
- What Are The Benefits Of IT Outsourcing?
- What's The Deal With Ransomware Attacks?
- Are GPON Providers Widely Available?
- What's GPON's Impact On Bandwidth?
- Why Is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
- How To Ensure Data Privacy Compliance?
 Blogs
Blogs Infographics
Infographics Videos
Videos Podcasts
Podcasts Case Studies
Case Studies Call For Quote
Call For Quote